This is a preprint.
Humanizing a CD28 signaling domain affects CD8 activation, exhaustion and stem-like precursors
- PMID: 40161835
- PMCID: PMC11952375
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.10.642460
Humanizing a CD28 signaling domain affects CD8 activation, exhaustion and stem-like precursors
Abstract
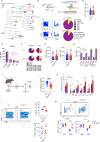
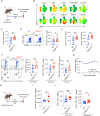
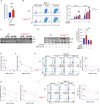
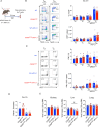
CD28 ligation provides critical signals that modulate activated T cell fate. In a human to mouse reverse-engineering approach, a single amino acid substitution adjacent to the C-terminal proline-rich domain created CD28A210P mice with enhanced signaling. CD28A210P mice experienced pro-inflammatory responses to CD28 superagonist antibody, analogous to severe cytokine storm induced in a human clinical trial, with a striking increase of activated CD8 T cells. In acute and chronic viral infections, early activation and expansion of CD28A210P CD8 effector T cells increased, with accelerated exhaustion in chronic infection. Mechanistically, CD28A210P enhanced JunB, IL-2, and inhibitory receptors driven by MEK1/2. Generation of CD28A210P stem-like progenitor (Tpex) cells was enhanced in acute and chronic infections, and further expanded by PD-L1 blockade in chronically-infected mice. Thus, 'humanized' PYAP mice reveal key roles for CD28 signaling strength in CD8 activation, accelerating exhaustion during antigen persistence, while promoting and sustaining Tpex during acute and chronic viral infection.
Figures


References
-
- Burr J. S. et al., Cutting edge: distinct motifs within CD28 regulate T cell proliferation and induction of Bcl-XL. J Immunol 166, 5331–5335 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Andres P. G. et al., Distinct regions in the CD28 cytoplasmic domain are required for T helper type 2 differentiation. Nat Immunol 5, 435–442 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
