Unveiling the placental bacterial microbiota: implications for maternal and infant health
- PMID: 40161970
- PMCID: PMC11949977
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1544216
Unveiling the placental bacterial microbiota: implications for maternal and infant health
Abstract
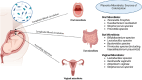
The human placenta is a unique organ that forms under specific physiological conditions and plays a crucial role in nutrient and metabolite exchange between the mother and fetus. Research on the placenta is important for understanding maternal-fetal diseases. Traditionally, the placenta was considered "sterile," but advancements in detection techniques have revealed the presence of a low level of microorganisms. This discovery challenges the traditional notion that the uterine placenta is sterile. The revelation of this truth marks a significant breakthrough in medical research, prompting more researchers to focus on this vital organ, the placenta. Placental microbial communities may originate from the oral, vaginal, and intestinal microbiota of expectant mothers. These microorganisms may reach the maternal-fetal interface, collectively shaping the placental microbiota and contributing to the composition of normal placental microbial communities. Abnormal placental microbial communities may be associated with some pregnancy complications and fetal developmental issues such as preterm birth, gestational hypertension, fetal growth restriction, and gestational diabetes mellitus. Intervention strategies targeting microbial communities, which include modulation of placental microbiota composition or function, such as probiotics, may help prevent or treat complications related to abnormal placental microbiota during pregnancy.
Keywords: infant health; maternal health; placental microbiota; pregnancy complications; source of placental microbiota.
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Chen, Chai, Yao and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources