Efficacy and safety of Lemborexant in treating adult patients with insomnia in China: a single-center, retrospective observational study
- PMID: 40162013
- PMCID: PMC11949819
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1495965
Efficacy and safety of Lemborexant in treating adult patients with insomnia in China: a single-center, retrospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Except for one case report, there has been no published study of Lemborexant treatment for patients with insomnia in China. This study investigated efficacy and safety of Lemborexant in treating Chinese patients with insomnia.
Methods: In this single-center, retrospective observational study, adult patients diagnosed with insomnia with an Insomnia Severity Index (ISI) score of ≥8 who were prescribed Lemborexant at Guangzhou United Family Hospital from January 2023 to July 2024 and who had ≥2 follow-up ISI assessment(s) were included. The primary outcome was change in the ISI total score from baseline after 4 weeks of Lemborexant treatment. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were collected.
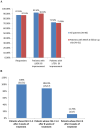
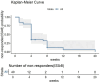
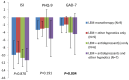
Results: Forty patients with a mean baseline ISI score of 17.0 ± 3.3 were included. The treatment continuation rate during the median 8-week (range: 2-20) follow-up was 90%. The ISI total score was reduced significantly from baseline after 4 weeks of treatment (-10.2 ± 3.0, p < 0.001), and was further reduced after 8 weeks of treatment (-12.7 ± 3.7, p < 0.001). Significant improvement in ISI total score at week 8 over week 4 was also observed. Both the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 and the General Anxiety Disorder-7 scores improved significantly after 4 weeks and 8 weeks of treatment. Thirty five (87.5%) patients were Lemborexant responders (ISI < 8). Age, combination therapy and Lemborexant 10 mg qn were independent factors associated with Lemborexant responders. One (2.5%) patient experienced mild dizziness. No patient discontinued the treatment due to TEAE(s).
Conclusion: Lemborexant treatment was effective and safe in treating a wide variety of Chinese patients with different symptom(s) of insomnia.
Keywords: Chinese patients; Lemborexant; insomnia; the general anxiety disorder-7; the insomnia severity index; the patient health questionnaire-9.
Copyright © 2025 Jian, Feng, Zhao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Lemborexant in Adults ≥ 65 Years of Age with Insomnia Disorder.Neurol Ther. 2024 Aug;13(4):1081-1098. doi: 10.1007/s40120-024-00622-9. Epub 2024 May 15. Neurol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38748321 Free PMC article.
-
Lemborexant for the Treatment of Insomnia in Patients From China: Four Case Studies.Cureus. 2024 Jul 16;16(7):e64655. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64655. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39149638 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of lemborexant treatment on insomnia severity: analyses from a 12-month study of adults with insomnia disorder.Sleep Med. 2022 Feb;90:249-257. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2022.01.024. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 35220140 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy of lemborexant and other insomnia treatments: a network meta-analysis.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Sep;27(9):1296-1308. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.21011. Epub 2021 Jun 12. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34121443 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of lemborexant vs placebo in treating adults with insomnia disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1976 patients.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04072-4. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40244447 Review.
References
-
- Kärppä M, Yardley J, Pinner K, Filippov G, Zammit G, Moline M, et al. . Long-term efficacy and tolerability of lemborexant compared with placebo in adults with insomnia disorder: results from the phase 3 randomized clinical trial SUNRISE 2. Sleep. (2020) 43:zsaa123. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsaa123, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg R, Murphy P, Zammit G, Mayleben D, Kumar D, Dhadda S, et al. . Comparison of Lemborexant with placebo and zolpidem tartrate extended release for the treatment of older adults with insomnia disorder: a phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2019) 2:e1918254. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.18254, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

