This is a preprint.
Type 1 Diabetes Polygenic Scores Improve Diagnostic Accuracy in Pediatric Diabetes Care
- PMID: 40162251
- PMCID: PMC11952484
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.06.25323229
Type 1 Diabetes Polygenic Scores Improve Diagnostic Accuracy in Pediatric Diabetes Care
Update in
-
Type 1 Diabetes Polygenic Scores Improve Diagnostic Accuracy in Pediatric Diabetes Care.Horm Res Paediatr. 2025 May 20:1-9. doi: 10.1159/000546445. Online ahead of print. Horm Res Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 40393445
Abstract
Background: Accurately classifying pediatric diabetes can be challenging for providers, and misclassification can result in suboptimal care. In recent years, type 1 diabetes (T1D) polygenic scores, which quantify one's genetic risk for T1D based on T1D risk allele burden, have been developed with good discriminating capacity between T1D and not-T1D. These tools have the potential to improve significantly diagnostic provider accuracy if used in clinic.
Methods: We applied T1D polygenic scores to a group of pediatric patients (n=1846) with genetic data available in the Boston Children's Hospital PrecisionLink Biobank, including 96 individuals diagnosed with T1D.
Results: Patients with a clinical diagnosis of T1D had higher T1D polygenic scores compared to controls (Wilcoxon rank-sum P<0.0001). Sixty-nine of the 74 individuals with diabetes and a T1D polygenic score exceeding an externally validated cutoff for distinguishing T1D from not-T1D were confirmed to have T1D. There were multiple cases where T1D polygenic scores would have clinical utility. An elevated T1D polygenic score suggested T1D in a pancreatic autoantibody (PAA)- negative individual with negative MODY genetic testing and a phenotype matching T1D. A low T1D polygenic score accurately indicated atypical diabetes in an individual found to have HNF1B-MODY. One individual had positive PAA, but the provider noted that the patient may not have classic T1D, as later suggested by a low T1D polygenic score.
Conclusion: T1D polygenic scores already have clinical utility to aid in the accurate diagnosis of pediatric diabetes. Efforts are now needed to advance their use in clinical practice.
Keywords: genetics; pediatric diabetes; polygenic scores.
Conflict of interest statement
MSU and JCF have received grant support from Novo Nordisk (unrelated to this manuscript). MSU has received royalties for contributions to UptoDate, Inc. JCF has participated on an advisory board for Alveus Therapeutics.
Figures
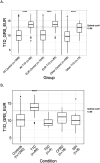

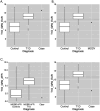
References
-
- Hathout EH, Thomas W, El-Shahawy M, Nahab F, Mace JW. Diabetic autoimmune markers in children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes. Pediatrics. 2001. Jun;107(6):E102. - PubMed
-
- Umpaichitra V, Banerji MA, Castells S. Autoantibodies in children with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002. Apr;15 Suppl 1:525–30. - PubMed
-
- Brooks-Worrell BM, Greenbaum CJ, Palmer JP, Pihoker C. Autoimmunity to islet proteins in children diagnosed with new-onset diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. May;89(5):2222–7. - PubMed
-
- Fornari E, Barbetti F, Iafusco D, Lombardo F, Miraglia Dal Giudice E, Rabbone I, et al. Type 2 diabetes in pediatrics. Minerva Pediatr (Torino). 2021. Dec;73(6):549–62. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
