Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with kidney stone disease: result from NHANES, 2007-2018
- PMID: 40162317
- PMCID: PMC11949785
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1537403
Association of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among individuals with kidney stone disease: result from NHANES, 2007-2018
Abstract
Background: The objective of this study is to investigate the relationship between the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and all-cause as well as cause-specific mortality among patients with kidney stones, and to evaluate the capability of NLR as a predictor of mortality.
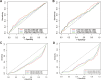
Methods: This study included 2,995 patients with kidney stones from the NHANES database during the period from 2007 to 2018, and subsequently linked this data with the National Death Index. The relationship between NLR and mortality was analyzed using the Cox proportional hazards model and Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Additionally, restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves were employed to explore the dose-response relationship between NLR and mortality, while time-dependent ROC curves were utilized to assess the predictive capability of NLR for mortality. Finally, the mediating effect of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) on the relationship between NLR and mortality was also analyzed.
Results: This study ultimately included 2,995 patients with kidney stones, with a median follow-up period of 74 months. A total of 395 deaths were recorded, of which 87 were attributed to cardiovascular diseases. An NLR cut-off of 3.62 was identified as significantly associated with survival outcomes using the 'maxstat' package and the principle of maximum rank statistics. The restricted cubic spline plot indicates a non-linear relationship between NLR and both all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality. After adjusting for relevant covariates, the Cox regression analysis demonstrated that, in comparison to the lower NLR group, the higher NLR group exhibited a 1.05-fold (HR 2.05, 95% CI 1.51-2.78, P < 0.001) increased risk of all-cause mortality and a 1.99-fold (HR 2.99, 95% CI 1.89-4.72, P < 0.001) increased risk of cardiovascular mortality. Furthermore, eGFR exhibited a significant mediating effect on the relationship between NLR and mortality.
Conclusion: This study found that patients with kidney stones exhibiting a high NLR have a significantly increased risk of mortality in the U.S. population. Therefore, monitoring NLR may be important for the prognosis of patients with kidney stones.
Keywords: NHANES; inflammation; kidney stone; mortality; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio.
Copyright © 2025 Chu, Wu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in coronary heart disease and hypertensive patients: a retrospective cohort study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 21;15:1442165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1442165. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39234507 Free PMC article.
-
Association between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with diabetes or prediabetes with comorbid obstructive sleep apnea symptoms: evidence from NHANES 2005-2008 and 2015-2018.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 22;16:1512621. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1512621. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40331136 Free PMC article.
-
Association between monocyte-lymphocyte ratio and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic kidney diseases: A data analysis from national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2003-2010.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2352126. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2352126. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38832474 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive role of neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and systemic immune-inflammation index for mortality in patients with MASLD.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 5;14(1):30403. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80801-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39638820 Free PMC article.
-
The Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cardiol Rev. 2025 May-Jun 01;33(3):202-211. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000820. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39531515
Cited by
-
The association between frailty index and all-cause mortality in US individuals with kidney stones: mediation by systemic immune-inflammation (SII) index.Urolithiasis. 2025 Aug 31;53(1):166. doi: 10.1007/s00240-025-01837-7. Urolithiasis. 2025. PMID: 40886263 Free PMC article.
-
Altered albumin/neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality for advanced cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 16;12:1595119. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1595119. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40740647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assasi N, Blackhouse G, Campbell K, Hopkins RB, Levine M, Richter T, et al. . Cadth Health Technology Assessments. Comparative Value of Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (Esr) and C-Reactive Protein (Crp) Testing in Combination Versus Individually for the Diagnosis of Undifferentiated Patients with Suspected Inflammatory Disease or Serious Infection: A Systematic Review and Economic Analysis. Ottawa (ON: Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health Copyright © CADTH 2015; (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

