Decoding m6Am by simultaneous transcription-start mapping and methylation quantification
- PMID: 40162895
- PMCID: PMC11957539
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.104139
Decoding m6Am by simultaneous transcription-start mapping and methylation quantification
Abstract
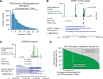
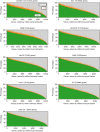
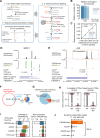
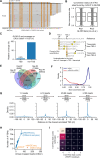
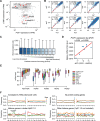
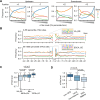
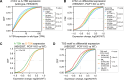
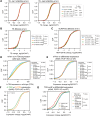
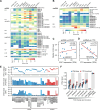
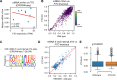
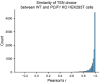
N 6,2'-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am) is a modified nucleotide located at the first transcribed position in mRNA and snRNA that is essential for diverse physiological processes. m6Am mapping methods assume each gene uses a single start nucleotide. However, gene transcription usually involves multiple start sites, generating numerous 5' isoforms. Thus, gene-level annotations cannot capture the diversity of m6Am modification in the transcriptome. Here, we describe CROWN-seq, which simultaneously identifies transcription-start nucleotides and quantifies m6Am stoichiometry for each 5' isoform that initiates with adenosine. Using CROWN-seq, we map the m6Am landscape in nine human cell lines. Our findings reveal that m6Am is nearly always a high stoichiometry modification, with only a small subset of cellular mRNAs showing lower m6Am stoichiometry. We find that m6Am is associated with increased transcript expression and provide evidence that m6Am may be linked to transcription initiation associated with specific promoter sequences and initiation mechanisms. These data suggest a potential new function for m6Am in influencing transcription.
Keywords: FTO; PCIF1; RNA modifications; biochemistry; chemical biology; human; m6Am; small nuclear RNA; transcription.
© 2024, Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
JL, LN No competing interests declared, BH Senior scientist in Engage Bio, SJ Co-founder and/or has equity in Chimerna Therapeutics, 858 Therapeutics, and Lucerna Technologies
Figures



Update of
-
Decoding m6Am by simultaneous transcription-start mapping and methylation quantification.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 21:2024.10.16.618717. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.16.618717. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Elife. 2025 Mar 31;13:RP104139. doi: 10.7554/eLife.104139. PMID: 39677659 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- An H, Hong Y, Goh YT, Koh CWQ, Kanwal S, Zhang Y, Lu Z, Yap PML, Neo SP, Wong C-M, Wong AST, Yu Y, Ho JSY, Gunaratne J, Goh WSS. m6Am sequesters PCF11 to suppress premature termination and drive neuroblastoma differentiation. Molecular Cell. 2024;84:4142–4157. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.10.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boulias K, Toczydłowska-Socha D, Hawley BR, Liberman N, Takashima K, Zaccara S, Guez T, Vasseur JJ, Debart F, Aravind L, Jaffrey SR, Greer EL. Identification of the m6Am Methyltransferase PCIF1 Reveals the Location and Functions of m6Am in the Transcriptome. Molecular Cell. 2019;75:631–643. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

