Modulation of CREB3L2-ATF4 heterodimerization via proteasome inhibition and HRI activation in Alzheimer's disease pathology
- PMID: 40164587
- PMCID: PMC11958753
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07586-0
Modulation of CREB3L2-ATF4 heterodimerization via proteasome inhibition and HRI activation in Alzheimer's disease pathology
Abstract
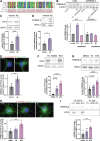
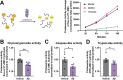
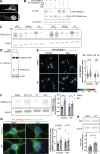
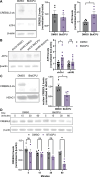
Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathology includes transcriptional changes in the neurons, which are in part caused by the heterodimerization of two stress response transcription factors, CREB3L2 and ATF4. We investigated the role of proteasome inhibition and the eIF2α-kinase HRI in the formation of CREB3L2-ATF4 in neurons exposed to soluble oligomeric Aβ42. While HRI activation increased ATF4 expression, it decreased CREB3L2 and CREB3L2-ATF4 levels. Proteasome inhibition, induced by Aβ42, leads to increased levels of both transcription factors in the nucleus. These findings suggest that CREB3L2 levels are normally kept low due to rapid degradation, but proteasome inhibition in response to Aβ42 disrupts this balance, increasing CREB3L2 and heterodimer levels. Activation of HRI not only reduced CREB3L2 and heterodimer levels but also prevented the transcriptional dysregulation of a CREB3L2-ATF4 target, SNX3. Our results suggest that manipulating the HRI pathway during proteasome inhibition could help restore normal gene expression in the context of AD-related protein accumulation.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations. The use of animals for this study was evaluated and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Columbia University (protocol AC-AABO8554).
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01NS121337/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- T32 NS064928/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- A2021030S/BrightFocus Foundation (BrightFocus)
- AARF-17-533511-RAPID/ALZ/Alzheimer's Association/United States
- T32NS064928/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

