Comparison of the efficacy of ultrasound-guided dextrose 25% hypertonic prolotherapy and intra-articular normal saline injection on pain, functional limitation, and range of motion in patients with knee osteoarthritis; a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40165187
- PMCID: PMC11956196
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-025-08580-5
Comparison of the efficacy of ultrasound-guided dextrose 25% hypertonic prolotherapy and intra-articular normal saline injection on pain, functional limitation, and range of motion in patients with knee osteoarthritis; a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background and aims: Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is a debilitating condition that manifests as knee pain and dysfunction. Clinicians prefer non-surgical options such as intra-articular injections for mild to moderate disease. Dextrose prolotherapy (DPTx) has been shown to have a beneficial effect on knee OA in the long-term. In this randomized controlled trial (RCT), we aimed to compare DPTx with intra-articular normal saline injection (IA-NS) to treat knee OA in terms of effectiveness and patient-reported outcomes.
Methods: The study was a double-blind RCT with an allocation ratio of 1:1. We used block randomization to assign patients to each treatment arm. Patients with a visual analog scale of at least 4 for pain, and a Kellgren-Lawrence scale of grade 2 or 3 (mild or moderate disease) were selected and assessed according to eligibility criteria. The participants received either 5 ml of 50% dextrose water or 5 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride. The patients were followed up at 2, 4, and 8 weeks. SPSS software was used for statistical analyses. All results were reported with a confidence interval of 95%, and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant.
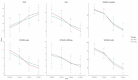
Results: Overall, 55 patients were included in the study, but 50 completed the study process (25 patients in each treatment arm). The mean age of patients with knee OA was 62.98 ± 5.37, ranging from 55 to 74 years. We observed significant improvement in both groups in terms of knee pain, function, and knee extension degree at all follow-up visits (p < 0.001). Although DPTx was associated with better results than IA-NS, the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). The adverse events were limited to injection-site pain and ecchymosis, which resolved by week 4.
Conclusion: Although we achieved slightly better results with DPTx, this treatment technique was not clinically or statistically superior to IA-NS in terms of knee pain and function in the short-term. Therefore, both DPTx and IA-NS are effective and well tolerated treatment options for knee OA. However, more RCTs are needed to confirm these claims.
Keywords: Dextrose; Intra-articular normal saline injection; Knee; Osteoarthritis; Prolotherapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Human ethics and consent to participate: The protocol for this study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences with the reference number IR.SUMS.MED.REC.1401.246. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants completed written informed consent before entering the study. They were provided with information regarding the goals of the study, treatment methods, alternative choices, and their probable adverse reactions prior to enrollment. It was clarified that patients were able to leave the study at any time they desired. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mathers DSC, Pfleger B. Global burden of osteoarthritis in the year 2000. World Health Organization; 2003.
-
- Stöhr H, Molday LL, Molday RS, Weber BH, Biedermann B, Reichenbach A, et al. Membrane-associated guanylate kinase proteins MPP4 and MPP5 associate with Veli3 at distinct intercellular junctions of the neurosensory retina. J Comp Neurol. 2005;481(1):31–41. - PubMed
-
- Hughes W, Goodall R, Salciccioli JD, Marshall DC, Davies AH, Shalhoub J, editors. ‘s Choice–Trends in lower extremity amputation incidence in European Union 15 + countries 1990–2017. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2020;60(4):602–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

