Effect of Biodegradable Microneedle Acupuncture in Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: a single-blinded randomized controlled pilot trial
- PMID: 40165880
- PMCID: PMC11933911
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2025.28.1.69
Effect of Biodegradable Microneedle Acupuncture in Mild to Moderate Atopic Dermatitis: a single-blinded randomized controlled pilot trial
Abstract
Objectives: The need for alternative therapies for atopic dermatitis (AD) has emerged due to the side effects of conventional therapies. Biodegradable microneedle acupuncture (BMA) is a novel medical device that overcame the shortcomings of traditional intradermal acupuncture (IDA), such as foreign body feeling and allergic dermatitis. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BMA for patients with Mild to Moderate AD compared with the IDA.
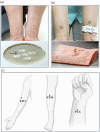
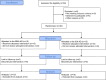
Methods: An assessor-blinded, parallel, non-superiority, randomized controlled pilot trial was conducted. Thirty adult participants were recruited from a single hospital and were equally divided into the experimental or control group. They were treated with BMA or IDA on both sides of LI11, ST36, and PC6 for four hours. Over four weeks, both interventions were performed eight times in total. The primary endpoint was the objective scoring AD (O-SCORAD) index. The secondary endpoints were visual analog scale (VAS) for itch and sleep disturbance, dermatology life quality index (DLQI), skin hydration, and transepidermal water loss (TEWL).
Results: Enrolled thirty participants completed the trial. After the trial, all endpoints remarkably improved compared with the baseline in both groups, except for the TEWL. Between the two interventions, there were no remarkable differences in the fourth week, except for the VAS score for itch and DLQI. No serious adverse events occurred during the study period.
Conclusion: Both BMA and IDA were effective in improving Mild to Moderate AD, and they were safe. BMA can be an alternative to conventional acupuncture for patients with sensitive skin, including metal allergies.
Keywords: atopic dermatitis; biodegradable microneedle acupuncture; efficacy; randomized controlled trial; thumbtack needle.
© 2025 Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Kim JW, Lee GH. Atopic dermatitis: basic and practice. Koonja; Paju: 2017. p. 484.
-
- Jo SJ, Kim CY, Ha U, Kwon K. Two case reports on atopic dermatitis with rebound phenomena after steroid interruption. J Korean Med Ophthalmol Otolaryngol Dermatol. 2021;34(1):101–11.
-
- Kong DY, Yang HJ, Pyun BY. The effects on treatment of atopic dermatitis with oral Lactobacillus casei supplements in Korean children. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2007;17(1):27–37.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
