Sodium citrate pretreatment enhances CAR-T cell persistence and anti-tumor efficacy through inhibition of calcium signaling
- PMID: 40165944
- PMCID: PMC11955688
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1540754
Sodium citrate pretreatment enhances CAR-T cell persistence and anti-tumor efficacy through inhibition of calcium signaling
Abstract
Introduction: Chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T) therapy has shown success in treating hematological malignancies, but its effectiveness against solid tumors is hindered by T cell exhaustion. During in vitro expansion, tonic signaling induced by CAR expression contributes to CAR-T cell exhaustion, which can be mitigated by inhibiting calcium signaling. Given that sodium citrate can chelate calcium ions and inhibit calcium signaling, in this study, we investigated whether sodium citrate could reduce exhaustion and enhance CAR-T cell function.
Methods: We constructed anti-CD70 CAR-T cells and cultured them in the presence of sodium citrate. The characteristics and functionality of sodium citrate-pretreated CAR-T cells were assessed through in vitro and in vivo experiments. To further validate our observation, we also treated anti-mesothelin (MSLN) CAR-T cells with sodium citrate and detected the phenotypes and anti-tumor function of CAR-T cells.
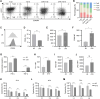
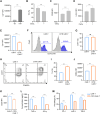
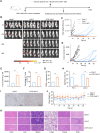
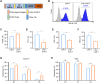
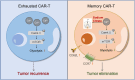
Results: We found that sodium citrate-pretreated anti-CD70 CAR-T cells exhibited reduced exhaustion, increased memory T cell proportions, and enhanced anti-tumor efficacy both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, sodium citrate treatment improved the in vivo persistence of CAR-T cells and prevented tumor recurrence. These beneficial effects were also observed in anti-MSLN CAR-T cells. Transcriptomic and metabolite analyses revealed that sodium citrate inhibited calcium signaling, mTORC1 activity, and glycolysis pathways, thus modulating T cell exhaustion and differentiation.
Discussion: Our findings suggest that sodium citrate supplementation during CAR-T cell expansion could be a promising strategy to improve CAR-T therapy for solid tumors by preventing exhaustion and promoting memory T cell formation.
Keywords: CAR-T; T cell exhaustion; calcium ions; cancer immunotherapy; sodium citrate; solid tumors.
Copyright © 2025 Yin, Chen, Ao, Xu, Cao, Huang, Liang, Hu, Liu, Wang, Li, Zhou, He and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
ZG is one of the inventors of a patent on the anti-CD70 CAR sequence employed in this work and the application number is 202410495812.1. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous targeting of Tim3 and A2a receptors modulates MSLN-CAR T cell antitumor function in a human cervical tumor xenograft model.Front Immunol. 2024 May 24;15:1362904. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1362904. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38855110 Free PMC article.
-
CD70 CAR-T cells empowered by TS-2021 through ex vivo transduction show potent antitumor efficacy against glioblastoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025 Jun 5;44(1):173. doi: 10.1186/s13046-025-03431-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40474210 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of adenosine 2A receptor improves the anti-tumor function of anti-mesothelin CAR T cells both in vitro and in vivo.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Dec 1;409(1):112886. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112886. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34673000
-
Optimizing CAR-T cell function in solid tumor microenvironment: insights from culture media additives.Curr Res Transl Med. 2025 Apr-Jun;73(2):103491. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2024.103491. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Curr Res Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39798497 Review.
-
Tonic signaling in CAR-T therapy: the lever long enough to move the planet.Front Med. 2025 Jun;19(3):391-408. doi: 10.1007/s11684-025-1130-x. Epub 2025 Mar 21. Front Med. 2025. PMID: 40117019 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

