This is a preprint.
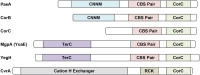
The CorC proteins MgpA (YoaE) and CorC protect from excess-cation stress and are required for egg white tolerance and virulence in Salmonella
- PMID: 40166170
- PMCID: PMC11957008
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.18.643926
The CorC proteins MgpA (YoaE) and CorC protect from excess-cation stress and are required for egg white tolerance and virulence in Salmonella
Abstract
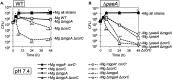
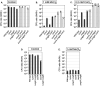
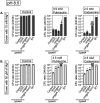
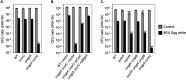
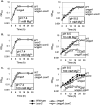
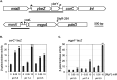
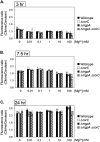
Cation homeostasis is a vital function. In Salmonella, growth in very low Mg2+ induces expression of high-affinity Mg2+ transporters and synthesis of polyamines, organic cations that substitute for Mg2+. Once Mg2+ levels are re-established, the polyamines must be excreted by PaeA. Otherwise, cells lose viability due to a condition we term excess-cation stress. We sought additional tolerance mechanisms for this stress. We show that CorC and MgpA (YoaE) are essential for survival in stationary phase after Mg2+ starvation. Deletion of corC causes a loss of viability additive with the paeA phenotype. Deletion of mgpA causes a synthetic defect in the corC background. This lethality is suppressed by loss of the inducible Mg2+ transporters, suggesting that the corC mgpA mutant is sensitive to changes in intracellular Mg2+. CorC and MgpA function independently of PaeA. A paeA mutant is sensitive to externally added polyamine in stationary phase; loss of CorC and MgpA suppressed this sensitivity. Conversely, the corC mgpA mutant, but not the paeA mutant, exhibited sensitivity to high Mg2+ and egg white. The corC mgpA mutant is also attenuated in a mouse model. The corC and mgpA genes are induced in response to increased Mg2+ concentrations. Thus, CorC and MgpA play some interrelated role in cation homeostasis. It is unlikely that these phenotypes are due to absolute levels of cations. Rather, the cell maintains relative concentrations of various cations that likely compete for binding to anionic components. Imbalance of these cations affects some essential function(s), leading to a loss of viability.
Keywords: Cations; Egg White; Magnesium; Polyamines; Salmonella; Stationary Phase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The CorC proteins MgpA (YoaE) and CorC protect from excess-magnesium stress and are required for egg white tolerance and virulence in Salmonella.mBio. 2025 Aug 18:e0202125. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02021-25. Online ahead of print. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40823839
-
Cation Homeostasis: Coordinate Regulation of Polyamine and Magnesium Levels in Salmonella.mBio. 2023 Feb 28;14(1):e0269822. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02698-22. Epub 2022 Dec 7. mBio. 2023. PMID: 36475749 Free PMC article.
-
PaeA (YtfL) protects from cadaverine and putrescine stress in Salmonella Typhimurium and E. coli.Mol Microbiol. 2021 Jun;115(6):1379-1394. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14686. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Mol Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33481283 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Structural Biology of Mg2+ Channels and Transporters.J Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 15;434(19):167729. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2022.167729. Epub 2022 Jul 13. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35841930 Review.
-
The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of cyclin M/CorC family of Mg2+ transporters.J Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Jan;148(1):14-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.09.004. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34924118 Review.
References
-
- Groisman EA, Kayser J, Soncini FC. 1997. Regulation of polymyxin resistance and adaptation to low-Mg2+ environments. Journal of Bacteriology 179:7040–7045. https://doi.org/doi:10.1128/jb.179.22.7040-7045.1997 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
