This is a preprint.
CTCF-RNA interactions orchestrate cell-specific chromatin loop organization
- PMID: 40166279
- PMCID: PMC11956997
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.03.19.643339
CTCF-RNA interactions orchestrate cell-specific chromatin loop organization
Update in
-
CTCF-RNA interactions orchestrate cell-specific chromatin loop organization.Sci Adv. 2025 Nov 28;11(48):eady5507. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ady5507. Epub 2025 Nov 26. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 41296854 Free PMC article.
Abstract
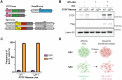
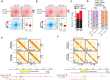
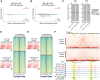
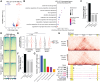
CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) is essential for chromatin organization. CTCF interacts with endogenous RNAs, and deletion of its ZF1 RNA-binding region (ΔZF1) disrupts chromatin loops in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs). However, the functional significance of CTCF-ZF1 RNA interactions during cell differentiation is unknown. Using an ESC-to-neural progenitor cell (NPC) differentiation model, we show that CTCF-ZF1 is crucial for maintaining cell-type-specific chromatin loops. Expression of CTCF-ΔZF1 leads to disrupted loops and dysregulation of genes within these loops, particularly those involved in neuronal development and function. We identified NPC-specific, CTCF-ZF1 interacting RNAs. Truncation of two such coding RNAs, Podxl and Grb10, disrupted chromatin loops in cis, similar to the disruption seen in CTCF-ΔZF1 expressing NPCs. These findings underscore the inherent importance of CTCF-ZF1 RNA interactions in preserving cell-specific genome structure and cellular identity.
Keywords: CTCF; RNA binding; chromatin loops; embryonic stem cells; gene expression; genome organization; neural progenitor cells.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS D.R. was a co-founder of Constellation Pharmaceuticals and Fulcrum Therapeutics. Currently, D.R has no affiliation with either company. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
