Detrimental effects of chronic arsenic exposure through daily diet on hepatic and renal health: An animal model study
- PMID: 40166734
- PMCID: PMC11957588
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101993
Detrimental effects of chronic arsenic exposure through daily diet on hepatic and renal health: An animal model study
Abstract
Background: Bangladesh is heavily impacted by arsenic contamination; however, in-depth research regarding the consequences of arsenic exposure through contaminated food remains in its nascent stage.
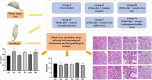
Objectives: Our study aimed to examine the effects of consuming arsenic-contaminated rice and vegetables on Wistar albino rats.
Methodology: A total of 30 Wistar albino rats were divided into control and experimental groups, receiving diets containing arsenic-contaminated rice and vegetable for 120 days. Arsenic levels in food samples were quantified using FI-HG-AAS. Hematological, biochemical, and histopathological analyses were conducted to assess hepatic and renal toxicity. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS, ANOVA, DMART with significance set at p < 0.05.
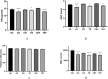
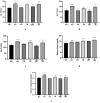
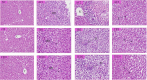
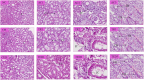
Findings: In hematological studies, hemoglobin was found to be significantly reduced in exposed rats (P < 0.05) to 13.67 ± 0.54 gm/dl for rice diet and 13.77 ± 0.28 gm/dl for edible fern diet compared to control (14.17 ± 0.43 gm/dl for rice diet and 15.27 ± 0.13 gm/dl for edible fern diet), and similar results were also observed for RBC and WBC. Elevated levels of serum ALT, AST, urea and creatinine reflected hepatic and renal dysfunction. In renal and hepatic tissue histopathology, inflammation, degeneration, and fatty changes were observed. This study provides the first direct evidence of systemic toxicity from chronic dietary arsenic exposure in Bangladesh, identifying rice and vegetables as significant, underrecognized sources of arsenic-related health risks.
Conclusion: We conclude that eating rice and vegetables that have been exposed to arsenic over an extended period of time might be harmful to the body.
Keywords: Arsenic; Edible fern; Naturally contaminated; Rice grain; Tissue histopathology; Wistar albino rats.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human health impact due to arsenic contaminated rice and vegetables consumption in naturally arsenic endemic regions.Environ Pollut. 2022 Sep 1;308:119712. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119712. Epub 2022 Jul 4. Environ Pollut. 2022. PMID: 35798190
-
Study of arsenic accumulation in rice and evaluation of protective effects of Chorchorus olitorius leaves against arsenic contaminated rice induced toxicities in Wistar albino rats.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016 Oct 14;17(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0091-8. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27737708 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
Arsenic levels in rice grain and assessment of daily dietary intake of arsenic from rice in arsenic-contaminated regions of Bangladesh--implications to groundwater irrigation.Environ Geochem Health. 2009 Apr;31 Suppl 1:179-87. doi: 10.1007/s10653-008-9238-x. Epub 2009 Jan 14. Environ Geochem Health. 2009. PMID: 19142738
-
Evaluating the efficacy and feasibility of post harvest methods for arsenic removal from rice grain and reduction of arsenic induced cancer risk from rice-based diet.Sci Total Environ. 2023 May 20;874:162443. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162443. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Sci Total Environ. 2023. PMID: 36858216 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO), Arsenic. WHO Fact Sheets, 2023. Available from: 〈https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic〉.
-
- Safiuddin M.D., Shirazi S.M., Yusoff S. Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bangladesh: a review. Int J. Phys. Sci. 2011;6(30):6791–6800. doi: 10.5897/IJPS11.1300. - DOI
-
- Hosen S.M., Das D., Kobi R., Chowdhury D.U., Alam M.J., Rudra B., Bakar M.A., Islam S., Rahman Z., Al-Forkan M. Study of arsenic accumulation in rice and evaluation of protective effects of Chorchorus olitorius leaves against arsenic contaminated rice induced toxicities in Wistar albino rats. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016;17:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s40360-016-0091-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

