Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the gut microbiome: pathogenic insights and therapeutic innovations
- PMID: 40166938
- PMCID: PMC11957707
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI186423
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and the gut microbiome: pathogenic insights and therapeutic innovations
Abstract
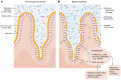
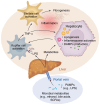
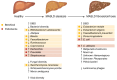
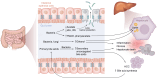
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a major cause of liver disease worldwide, and our understanding of its pathogenesis continues to evolve. MASLD progresses from steatosis to steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis, and this Review explores how the gut microbiome and their metabolites contribute to MASLD pathogenesis. We explore the complexity and importance of the intestinal barrier function and how disruptions of the intestinal barrier and dysbiosis work in concert to promote the onset and progression of MASLD. The Review focuses on specific bacterial, viral, and fungal communities that impact the trajectory of MASLD and how specific metabolites (including ethanol, bile acids, short chain fatty acids, and other metabolites) contribute to disease pathogenesis. Finally, we underscore how knowledge of the interaction between gut microbes and the intestinal barrier may be leveraged for MASLD microbial-based therapeutics. Here, we include a discussion of the therapeutic potential of prebiotics, probiotics, postbiotics, and microbial-derived metabolites.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

