N4-acetylcytidine coordinates with NP1 and CPSF5 to facilitate alternative RNA processing during the replication of minute virus of canines
- PMID: 40167508
- PMCID: PMC11959542
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaf229
N4-acetylcytidine coordinates with NP1 and CPSF5 to facilitate alternative RNA processing during the replication of minute virus of canines
Abstract
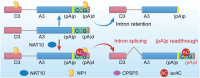
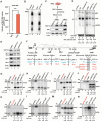
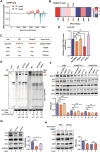
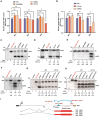
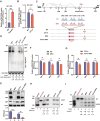
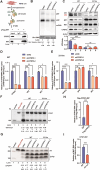
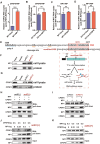
RNA modifications play crucial roles in RNA metabolism, structure, and functions. N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) modifications have been shown to enhance stability and translation efficiency of messenger RNAs and viral RNAs. However, the relationship between ac4C and alternative RNA processing remains unexplored. Here, N-acetyltransferase 10 (NAT10) and its catalyzed ac4C modifications on minute virus of canines (MVC) were shown to regulate viral DNA replication and RNA processing, including both the alternative RNA splicing and polyadenylation. Through acRIP-seq and RedaC:T-seq, functional ac4C-modified residue 3311 was identified and characterized, which affected MVC RNA processing rather than altered the viral RNA stability. Ac4C modification at nt 3311 was revealed to participate in NP1-mediated viral RNA processing without influencing RNA affinity of NP1. Meanwhile, CPSF5 was identified to interact with NP1 and mediate viral RNA processing in an ac4C-dependent manner. Further in vitro assays showed that NP1 recruited CPSF5 to MVC RNAs, and the ac4C modification promoted specific binding of CPSF5 to the target region, which ensured precise alternative MVC RNA processing. This study not only reveals the functions of NAT10 and ac4C but also elucidates the mechanisms by which RNA modifications orchestrate MVC proteins and host factors for efficient viral replication and alternative RNA processing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

