Intraoperative phrenic nerve stimulation to prevent diaphragm fiber weakness during thoracic surgery
- PMID: 40168300
- PMCID: PMC11961012
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0320936
Intraoperative phrenic nerve stimulation to prevent diaphragm fiber weakness during thoracic surgery
Abstract
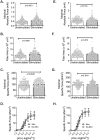
Thoracic surgery rapidly induces weakness in human diaphragm fibers. The dysfunction is thought to arise from combined effects of the surgical procedures and inactivity. This project tested whether brief bouts of intraoperative hemidiaphragm stimulation would mitigate slow and fast fiber loss of force in the human diaphragm. We reasoned that maintenance of diaphragm activity with brief bouts of intraoperative phrenic stimulation would mitigate diaphragm fiber weakness and myofilament protein derangements caused by thoracic surgery. Nineteen adults (9 females, age 59 ± 12 years) with normal inspiratory strength or spirometry consented to participate. Unilateral phrenic twitch stimulation (twitch duration 1.5 ms, frequency 0.5 Hz, current 2x the motor threshold, max 25 mA) was applied for one minute, every 30 minutes during cardiothoracic surgery. Thirty minutes following the last stimulation bout, biopsies were obtained from the hemidiaphragms for single fiber force mechanics and quantitation of myofilament proteins (abundance and phosphorylation) and compared by a linear mixed model and paired t-test, respectively. Subjects underwent 6 ± 2 hemidiaphragm stimulations at 17 ± 6 mA, during 278 ± 68 minutes of surgery. Longer-duration surgeries were associated with a progressive decline in diaphragm fiber force (p < 0.001). In slow-twitch fibers, phrenic stimulation increased absolute force (+25%, p < 0.0001), cross-sectional area (+16%, p < 0.0001) and specific force (+7%, p < 0.0005). Stimulation did not alter contractile function of fast-twitch fibers, calcium-sensitivity in either fiber type, and abundance and phosphorylation of myofilament proteins. In adults without preoperative weakness or lung dysfunction, unilateral phrenic stimulation mitigated diaphragm slow fiber weakness caused by thoracic surgery, but had no effect on myofilament protein abundance or phosphorylation.
Copyright: © 2025 Bresciani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Hulzebos EHJ, Helders PJM, Favié NJ, De Bie RA, Brutel de la Riviere A, Van Meeteren NLU. Preoperative intensive inspiratory muscle training to prevent postoperative pulmonary complications in high-risk patients undergoing CABG surgery: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2006;296(15):1851–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.15.1851 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dres M, Dubé B-P, Mayaux J, Delemazure J, Reuter D, Brochard L, et al.. Coexistence and impact of limb muscle and diaphragm weakness at time of liberation from mechanical ventilation in medical intensive care unit patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(1):57–66. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201602-0367OC - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

