Performance of qpAdm-based screens for genetic admixture on graph-shaped histories and stepping stone landscapes
- PMID: 40169722
- PMCID: PMC12118350
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf047
Performance of qpAdm-based screens for genetic admixture on graph-shaped histories and stepping stone landscapes
Abstract
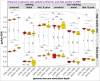
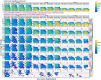
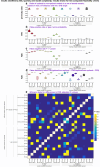
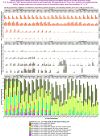
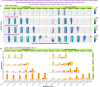
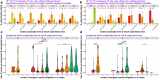
qpAdm is a statistical tool that is often used for testing large sets of alternative admixture models for a target population. Despite its popularity, qpAdm remains untested on 2D stepping stone landscapes and in situations with low prestudy odds (low ratio of true to false models). We tested high-throughput qpAdm protocols with typical properties such as number of source combinations per target, model complexity, model feasibility criteria, etc. Those protocols were applied to admixture graph-shaped and stepping stone simulated histories sampled randomly or systematically. We demonstrate that false discovery rates of high-throughput qpAdm protocols exceed 50% for many parameter combinations since: (1) prestudy odds are low and fall rapidly with increasing model complexity; (2) complex migration networks violate the assumptions of the method; hence, there is poor correlation between qpAdm P-values and model optimality, contributing to low but nonzero false-positive rate and low power; and (3) although admixture fraction estimates between 0 and 1 are largely restricted to symmetric configurations of sources around a target, a small fraction of asymmetric highly nonoptimal models have estimates in the same interval, contributing to the false-positive rate. We also reinterpret large sets of qpAdm models from 2 studies in terms of source-target distance and symmetry and suggest improvements to qpAdm protocols: (1) temporal stratification of targets and proxy sources in the case of admixture graph-shaped histories, (2) focused exploration of few models for increasing prestudy odds; and (3) dense landscape sampling for increasing power and stringent conditions on estimated admixture fractions for decreasing the false-positive rate.
Keywords: qpAdm; admixture graphs; archaeogenetics; genetic admixture; simulation; stepping stone models.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Genetics Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: The author(s) declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Update of
-
Performance of qpAdm-based screens for genetic admixture on admixture-graph-shaped histories and stepping-stone landscapes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 3:2023.04.25.538339. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.25.538339. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Genetics. 2025 May 8;230(1):iyaf047. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyaf047. PMID: 37904998 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

