The effects of transdermal estrogens combined with Medroxyprogesterone Acetate on cardiovascular disease risk factors in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40170070
- PMCID: PMC11959720
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-025-01664-1
The effects of transdermal estrogens combined with Medroxyprogesterone Acetate on cardiovascular disease risk factors in postmenopausal women: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: To date, no meta-analysis has reported on the role of transdermal estrogens combined with Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (MPA) in relation to cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors in postmenopausal women. To fill this knowledge gap, a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) was conducted to assess the effects of transdermal estrogens and MPA on CVD risk factors in postmenopausal women.
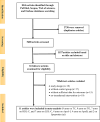
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in major databases including PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, SCOPUS, and Embase, from inception to 12 February 2025. The combination of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and non-MeSH keywords was used.
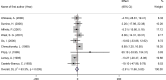
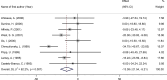
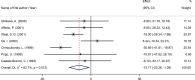
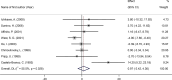
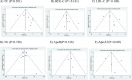
Results: A total of 14 trials were included in the meta-analysis. The combined eligible trials found that transdermal estrogens combined with MPA significantly decreased total cholesterol (TC) (WMD: -13.37 mg/dL, 95% CI: -21.54 to -5.21, p = 0.001), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) (WMD: -12.17 mg/dL, 95% CI: -23.26 to -1.08, p = 0.031), and apolipoprotein B (ApoB) (WMD: -7.26 mg/dL, 95% CI: -11.48 to -3.03, p = 0.001) compared to the control. No statistically significant associations were observed between transdermal estrogens combined with MPA on triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), and apolipoprotein A1 (ApoAI).
Conclusion: Based on the results of the current meta-analysis, transdermal estrogens combined with oral MPA administration had a beneficial effect on certain CVD risk factors in postmenopausal women, as evidenced by the significant reductions in TC, LDL-C, and ApoB.
Keywords: Apolipoproteins; Cholesterol; Lipid profile; Lipoprotein(a); Postmenopausal women; Transdermal estrogens combined with oral Medroxyprogesterone acetate; Triglycerides.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lindstrom M, DeCleene N, Dorsey H, Fuster V, Johnson CO, LeGrand KE, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risks collaboration, 1990–2021. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;80(25):2372–425. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Chen X, Gong X, He D, Cheng X, Prabahar K, et al. The effect of 17beta-estradiol plus Norethisterone acetate on anthropometric indices: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2023;287:176–85. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

