Astragaloside IV accelerates hematopoietic reconstruction by improving the AMPK/PGC1α-mediated mitochondrial function in hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 40170084
- PMCID: PMC11963557
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01092-3
Astragaloside IV accelerates hematopoietic reconstruction by improving the AMPK/PGC1α-mediated mitochondrial function in hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Radiotherapy can damage hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) in bone marrow, leading to impaired hematopoietic function. Current treatments mainly target differentiated hematopoietic progenitor cells, which may accelerate their depletion. Astragaloside IV (AS-IV), derived from Astragalus membranaceus, shows potential in hematopoiesis, but its direct effects on HSC remain unclear.
Methods: The study employed both in vitro and in vivo approaches. In vitro experiments utilized K562 cells and mouse bone marrow nucleated cells (BMNCs) to evaluate AS-IV's effects on cell proliferation and mitochondrial function. In vivo studies involved a 4.0 Gy total body irradiation mouse model treated with different doses of AS-IV (50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg). The mechanism of action was investigated through Western blot, flow cytometry, and metabolomics analyses. The AMPK/PGC1α pathway regulation was verified using AMPK inhibitors and mutant plasmid, with molecular docking confirming AS-IV's direct binding to AMPK.
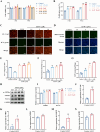
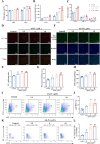
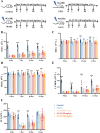
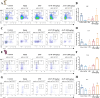
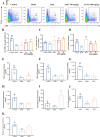
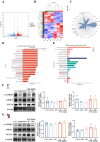
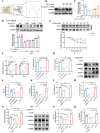
Results: In vitro studies demonstrated that AS-IV significantly promoted the proliferation of K562 cells and BMNC while enhancing their mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondrial mass, and ATP production. In the irradiated mouse model, AS-IV treatment led to significant improvements in peripheral blood cell counts, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and hemoglobin levels. Further investigation revealed that AS-IV increased the proportion of HSC in both bone marrow and spleen while improving their mitochondrial function. Transcriptomic sequencing and Western blot analysis identified the AMPK/PGC1α signaling pathway as the key mechanism underlying AS-IV-mediated mitochondrial enhancement. These findings were validated through pharmacological inhibition of AMPK and AMPKK45R mutation experiments.
Conclusion: AS-IV accelerates hematopoietic reconstruction following radiation injury via activation of the AMPK/PGC1α signaling pathway, which enhances HSC mitochondrial function.
Keywords: AMPK/PGC1α pathway; Astragaloside IV; Hematopoietic stem cells; Mitochondrial function.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal study protocol was approved by the laboratory animal ethics committee of Southwest Medical University (License NO.20220812-029). Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish the manuscript. Competing interests: No potential competing interests were reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Dainiak N, Waselenko JK, Armitage JO, et al. The hematologist and radiation casualties. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2003;(1):473–496. 10.1182/asheducation-2003.1.473. - PubMed
-
- De Ruysscher D, Niedermann G, Burnet NG, et al. Radiotherapy toxicity. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):13. 10.1038/s41572-019-0064-5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

