Effect of deviated nasal septum on Eustachian tube dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40170469
- PMCID: PMC12324937
- DOI: 10.1017/S0022215125000325
Effect of deviated nasal septum on Eustachian tube dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: A range of chronic ear complaints may be attributed to Eustachian tube dysfunction. Eustachian tube dysfunction secondary to a deviated nasal septum has been described in several clinical studies, with symptomatic improvement demonstrated following septoplasty. However, uncertainty exists as to the size of the effect and consistency between studies.
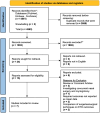
Methods: Electronic searches were carried out of Pubmed, Embase and the Cochrane Library for adult patients with complaints of nasal obstruction and/or impairment and/or complaints of ear fullness undergoing nasal surgery.
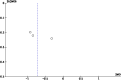
Results: Seven studies met the inclusion criteria. Studies evaluated the effect of nasal surgery on Eustachian tube dysfunction using a variety of outcomes, including Eustachian tube function tests, the Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire-7, tympanometry and Nasal Obstruction Symptom Evaluation scores. The results demonstrated the positive impact of nasal surgery on various outcomes related to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Conclusion: Nasal surgery has been demonstrated to have promising results as a therapeutic option for patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction and a deviated nasal septum, offering significant symptom relief and improved quality of life. Through the integration of the treatment of nasal symptoms in the management of Eustachian tube dysfunction, clinicians can adopt a comprehensive approach to addressing the underlying pathologies contributing to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Keywords: Eustachian tube dysfunction; deviated nasal septum; nasal surgery; septoplasty.
Figures

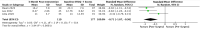

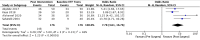


References
-
- Farooqi S, Saqulain G, Mumtaz N. Effect of nasal surgery on Eustachian tube function and middle ear ventilation. Isra Med J 2018;10:336–9
-
- Lee IH, Kim DH, Kim SW, Kim SW. Changes in symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction after nasal surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2022;279:5017–23 - PubMed
-
- Lima AF, Moreira FC, Costa IE, Azevedo C, Mar F, Dias L. Nasal septum deviation and Eustachian tube function: a prospective case-control study based on tympanometry, tubomanometry, and ETDQ-7. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2022;73:35–41 - PubMed
-
- Salvinelli F, Casale M, Greco F, D’Ascanio L, Petitti T, Di Peco V. Nasal surgery and Eustachian tube function: effects on middle ear ventilation. Clin Otolaryngol 2005;30:409–13 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

