Knee focal cartilage defect location heat map and local surface morphology characterisation: Insights for focal knee resurfacing implant design
- PMID: 40170715
- PMCID: PMC11960246
- DOI: 10.1002/jeo2.70216
Knee focal cartilage defect location heat map and local surface morphology characterisation: Insights for focal knee resurfacing implant design
Abstract
Purpose: The objective of this work was to characterise the dimensions of knee focal cartilage defects, generate a heat map of cartilage defect locations, and characterise the native articular surface morphology at the most common defect sites to aid in the design of generic focal knee resurfacing implants (FKRIs).
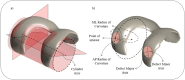
Methods: Healthy femoral cartilage was segmented from knee magnetic resonance imaging scans of 70 patients eligible for FKRI surgery. Cartilage defects were manually reconstructed to create three-dimensional (3D) native cartilage and cartilage defect models. A 3D statistical shape model of the native cartilage was created and 200 artificial models with varying shapes were generated. A heat map showing the frequency of defect occurrence location was created, and the size and aspect ratio of the defects were determined. Local radii of curvature were calculated at five locations that exhibit high defect occurrence for the medial and lateral condyles and in the trochlear groove.
Results: The median defect size and aspect ratio were 2.7 and 1.6, respectively. Cartilage defect location frequency heat maps were successfully generated for the medial and lateral condyles. The median mediolateral and anteroposterior radius of curvature at the medial condyle hotspot were 17.5 mm and 40.8 mm respectively, and 22.6 mm and 33.8 mm at the lateral condyle hotspot.
Conclusions: Characteristics of knee focal cartilage defect properties such as the size, their spatial distribution and local articular cartilage surface morphology offer valuable insights for the design of generic FKRIs.
Level of evidence: Level IV.
Keywords: cartilage defect location heat map; cartilage surface morphology; knee focal cartilage defects; lateral femoral condyle; medial femoral condyle; statistical shape modelling; trochlea.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Pieter Emans and Alex Roth are shareholders of Avalanche Medical BV, a commercial entity developing a focal knee resurfacing implant. Erkan Aşık is an employee of Avalanche Medical BV. Pieter Emans has a consultancy agreement with Episurf Medical AB.
Figures





References
-
- Ajdari N, Tempelaere C, Masouleh MI, Abel R, Delfosse D, Emery R, et al. Hemiarthroplasties: the choice of prosthetic material causes different levels of damage in the articular cartilage. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2020;29:1019–1029. - PubMed
-
- Audenaert EA, Van Houcke J, Almeida DF, Paelinck L, Peiffer M, Steenackers G, et al. Cascaded statistical shape model based segmentation of the full lower limb in CT. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22:644–657. - PubMed
-
- Becher C, Megaloikonomos PD, Lind M, Eriksson K, Brittberg M, Beckmann J, et al. High degree of consensus amongst an expert panel regarding focal resurfacing of chondral and osteochondral lesions of the femur with mini‐implants. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2023;31:4027–4034. - PubMed
-
- Berkmortel C, Langohr GDG, King G, Johnson J. Hemiarthroplasty implants should have very low stiffness to optimize cartilage contact stress. J Orthop Res. 2020;38:1719–1726. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

