Brainwide mesoscale functional networks revealed by focal infrared neural stimulation of the amygdala
- PMID: 40170996
- PMCID: PMC11960096
- DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwae473
Brainwide mesoscale functional networks revealed by focal infrared neural stimulation of the amygdala
Abstract
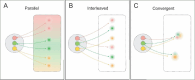
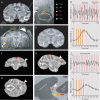
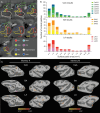
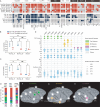
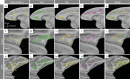
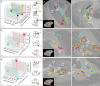
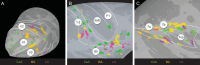
The primate amygdala serves to evaluate the emotional content of sensory inputs and modulate emotional and social behaviors; it modulates cognitive, multisensory and autonomic circuits predominantly via the basal, lateral and central nuclei, respectively. Recent evidence has suggested the mesoscale (millimeter-scale) nature of intra-amygdala functional organization. However, the connectivity patterns by which these mesoscale regions interact with brainwide networks remain unclear. Using infrared neural stimulation of single mesoscale sites coupled with mapping in ultrahigh field 7-T functional magnetic resonance imaging, we have discovered that these mesoscale sites exert influence over a surprisingly extensive scope of the brain. Our findings strongly indicate that mesoscale sites within the amygdala modulate brainwide networks through a 'one-to-many' (integral) way. Meanwhile, these connections exhibit a point-to-point (focal) topography. Our work provides new insights into the functional architecture underlying emotional and social behavioral networks, thereby opening up possibilities for individualized modulation of psychological disorders.
Keywords: amygdala; brainwide network; connectional topography; infrared neural stimulation; intra-individual datasets; mesoscale topography; ultrahigh field fMRI.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of China Science Publishing & Media Ltd.
Figures
Update of
-
Brainwide mesoscale functional networks revealed by focal infrared neural stimulation of the amygdala.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 6:2024.02.14.580397. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.14.580397. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Natl Sci Rev. 2024 Dec 24;12(4):nwae473. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwae473. PMID: 38464165 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Adolphs R, Anderson DJ. The neuroscience of emotion in humans. The Neuroscience of Emotion. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2018. 251–78.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
