A novel grid-assisted pie-crusting technique for achieving soft tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty
- PMID: 40171007
- PMCID: PMC11958710
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1566642
A novel grid-assisted pie-crusting technique for achieving soft tissue balance in total knee arthroplasty
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the effectiveness of a novel grid-based pie-crusting technique for soft tissue release at different locations of the medial collateral ligament (MCL) during total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
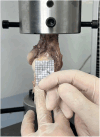
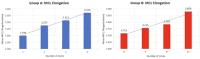
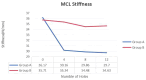
Methods: Twelve fresh-frozen cadaveric knee joints were dissected. A novel grid was designed to cover the entire surface of the MCL. The specimens were divided into two groups: Group A, where only the central portion of the ligament underwent pie-crusting release, and Group B, where selective release targeted the femoral and tibial attachment points of the MCL. Mechanical testing was conducted via a Shimadzu AG-X precision instrument. Each group underwent twelve punctures, and data were collected to calculate deformation and stiffness metrics. The mean elongation and stiffness values were analyzed, and regression analysis was performed to evaluate correlations between the number of punctures and changes in elongation and stiffness.
Results: No significant differences in initial stiffness were observed between the two groups (P = 0.42). Following 12 punctures, the stiffness decreased by 6.47 ± 4.06 N/mm in Group A and 1.08 ± 1.32 N/mm in Group B (P = 0.006). Despite this disparity in stiffness reduction, no significant differences in MCL elongation were observed between the groups. Group A demonstrated an elongation of 0.171 ± 0.180 mm, whereas Group B exhibited an elongation of 0.164 ± 0.123 mm (P = 0.47). A linear relationship was identified between stiffness reduction and the number of punctures (R 2 = 0.61 ± 0.29), as well as between ligament elongation and the number of punctures (R 2 = 0.89 ± 0.09).
Conclusion: The grid-assisted pie-crusting technique, which uniformly covers the MCL, enables precise and controlled soft tissue release. This approach provides valuable insights for clinicians performing MCL release during TKA, facilitating improved soft tissue balance and potentially enhancing surgical outcomes.
Keywords: TKA; arthroplasty; medial collateral ligament; pie-crusting; soft tissue balancing.
© 2025 Cheng, Wang, Liu, Mu, Wang, Lin, Yin and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mehdikhani KG, Moreno BM, Reid JJ, de Paz Nieves A, Lee Y-Y, Della Valle AG. An algorithmic, pie-crusting medial soft tissue release reduces the need for constrained inserts patients with severe varus deformity undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. (2016) 31(7):1465–9. 10.1016/j.arth.2016.01.006 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

