Correlation between cardiometabolic index and psoriasis: a cross-sectional analysis using NHANES data
- PMID: 40171114
- PMCID: PMC11959033
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1552269
Correlation between cardiometabolic index and psoriasis: a cross-sectional analysis using NHANES data
Abstract
Background: Psoriasis is closely associated with metabolic health. The Cardiometabolic Index (CMI) is an innovative and easily obtainable metric employed to assess cardiometabolic health. This study aims to examine the possible relationship between CMI and psoriasis.
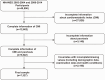
Methods: Data from four successive cycles of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) conducted between 2003-2004 and 2009-2014 were employed. This encompassed adults with self-reported psoriasis diagnoses and comprehensive information necessary for calculating the CMI. The calculation formula for CMI is Triglycerides (TG)/High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) × WHtR (WHtR = waist circumference/height). A multivariable logistic regression model was utilized to examine the linear relationship between CMI and psoriasis. Subgroup analyses were conducted to investigate potential contributing factors. The linear relationship was further established using smooth curve fitting.
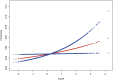
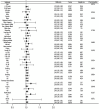
Results: This study, utilizing NHANES data, comprised a cohort of 7,327 American adults. The multivariable logistic regression analysis indicated that in the fully adjusted model, people with the greatest CMI had a 71% increased probability of psoriasis relative to those with the lowest CMI (OR = 1.71; 95% CI, 1.11-2.61, P < 0.05). Smooth curve fitting demonstrated a linear connection between CMI and psoriasis (P < 0.05). The subgroup analysis revealed no significant interactions between CMI and specific subgroups (all interactions P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Our research indicates a substantial linear correlation between CMI and psoriasis in American adults. This method facilitates the identification of groups at increased risk for psoriasis, therefore guiding therapeutic solutions and public health activities to improve metabolic and dermatological health outcomes.
Keywords: NHANES; cardiometabolic index; cross-sectional study; multivariate logic analysis; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Gan, Cheng and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alshahrani J. A., Alshahrani A. M., Ali Alshahrani S., Abdullah Alshahrani F., Saeed Matar Alzahrani M., Jaza Albalawi R., et al. (2023). A holistic view of psoriasis: examining its association with dyslipidemia and obesity in a decade-long systematic review and meta-analysis. Cureus 15, e49241. 10.7759/cureus.49241 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

