Understanding the role of trehalose in interactions between Wolbachia and Aedes aegypti
- PMID: 40171161
- PMCID: PMC11958977
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1547873
Understanding the role of trehalose in interactions between Wolbachia and Aedes aegypti
Abstract
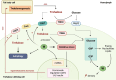
Mosquito-borne diseases such as chikungunya, dengue, and Zika represent a major burden on global public health. To fight against these arboviruses, vector control strategies are a priority. One existing strategy is based on the use of an endosymbiotic bacterium, Wolbachia, which reduces the transmission of arboviruses by the mosquito Aedes aegypti via a pathogen blocking effect. Wolbachia in Ae. aegypti disrupts several pathways of the host's metabolism. Trehalose is a carbohydrate circulating mainly in insect hemolymph and plays a role in numerous mechanisms as energy source or stress recovery molecule and in chitin synthesis. This study explores the importance of trehalose in the interactions between Wolbachia and Ae. aegypti, and attempts to understand the pathogen blocking effect.
Keywords: Aedes aegypti; Wolbachia; antioxidant; autophagy; pathogen-blocking effect; trehalose.
Copyright © 2025 Dupuis, Pocquet and Failloux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aedes Anphevirus: an Insect-Specific Virus Distributed Worldwide in Aedes aegypti Mosquitoes That Has Complex Interplays with Wolbachia and Dengue Virus Infection in Cells.J Virol. 2018 Aug 16;92(17):e00224-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00224-18. Print 2018 Sep 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29950416 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Symbiotic Genome-Scale Model Reveals Wolbachia's Arboviral Pathogen Blocking Mechanism in Aedes aegypti.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0156321. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01563-21. Epub 2021 Oct 12. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34634928 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Wolbachia-infected mosquito deployments in reducing the incidence of dengue and other Aedes-borne diseases in Niterói, Brazil: A quasi-experimental study.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Jul 12;15(7):e0009556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009556. eCollection 2021 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34252106 Free PMC article.
-
Wolbachia-mediated virus blocking in the mosquito vector Aedes aegypti.Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2017 Aug;22:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2017.05.005. Epub 2017 May 10. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2017. PMID: 28805637 Review.
-
Mission Accomplished? We Need a Guide to the 'Post Release' World of Wolbachia for Aedes-borne Disease Control.Trends Parasitol. 2018 Mar;34(3):217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2017.11.011. Epub 2018 Jan 23. Trends Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29396201 Review.
References
-
- Asgarian T. S., Vatandoost H., Hanafi-Bojd A. A., Nikpoor F. (2023). Worldwide Status of Insecticide Resistance of Aedes aEgypti and Ae. albopictus, Vectors of Arboviruses of Chikungunya, Dengue, Zika and Yellow Fever. J. Arthropod-Borne Dis. 17, 1–27. doi: 10.18502/jad.v17i1.13198 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

