Generation of inositol polyphosphates through a phospholipase C-independent pathway involving carbohydrate and sphingolipid metabolism in Trypanosoma cruzi
- PMID: 40172212
- PMCID: PMC12077091
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.03318-24
Generation of inositol polyphosphates through a phospholipase C-independent pathway involving carbohydrate and sphingolipid metabolism in Trypanosoma cruzi
Abstract
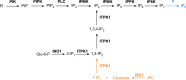
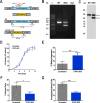
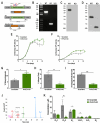
Inositol phosphates are involved in a myriad of biological roles and activities such as Ca2+ signaling, phosphate homeostasis, energy metabolism, and disease pathogenicity. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, synthesis of inositol phosphates occurs through the phosphoinositide phospholipase C (PLC)-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol and further IP3 phosphorylation by additional kinases that leads to the formation of highly phosphorylated inositol derivatives, known as inositol pyrophosphates. Inositol-tetrakisphosphate 1-kinase (ITPK1) is an enzyme that mediates a PLC-independent inositol polyphosphate synthesis through phosphorylation of inositol monophosphates and other intermediates in the cytosol. In this work, we identified and characterized a Trypanosoma cruzi ITPK1 (TcITPK1) homolog. The ability of TcITPK1 to act as the mediator for this alternative pathway was established through plc1Δ and plc1Δ isc1Δ yeast complementation assays and SAX-HPLC analyses of radioactively labeled inositol. TcITPK1 localizes to the cytosol, and knockout attempts of TcITPK1 revealed that only one allele was replaced by the DNA donor cassette at the specific locus, suggesting that null alleles may have lethal effects in epimastigotes. Ablation of T. cruzi phosphoinositide phospholipase C 1 (TcPI-PLC1) affected the synthesis of IP3 from glucose 6-phosphate but did not affect the synthesis of inositol polyphosphates, while ablation of inositol phosphosphingolipid phospholipase (TcISC1) affected the synthesis of inositol polyphosphates, thus revealing that the PLC-independent pathway using either glucose 6-phosphate or inositol phosphoceramide is involved in the synthesis of inositol polyphosphates, while the PLC-dependent pathway is involved in IP3 formation needed for Ca2+ signaling.
Importance: Millions of people are infected with Trypanosoma cruzi, and the current treatment is not satisfactory. Inositol pyrophosphates have been established as important signaling molecules. Our work demonstrates the presence of a phospholipase C-independent pathway for the synthesis of inositol pyrophosphates in T. cruzi. Furthermore, we demonstrate that this pathway starts with the synthesis of inositol monophosphates from glucose 6-phosphate or from inositol phosphoceramide, linking it to carbohydrate and sphingolipid metabolism. The essentiality of the pathway for the survival of T. cruzi infective stages makes it an ideal drug target for treating American trypanosomiasis.
Keywords: Trypanosoma cruzi; inositol phosphoceramide; inositol pyrophosphates; phospholipase C; sphingolipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
ITPK1 mediates the lipid-independent synthesis of inositol phosphates controlled by metabolism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Dec 3;116(49):24551-24561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1911431116. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31754032 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol pyrophosphates modulate S phase progression after pheromone-induced arrest in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):1717-25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.412288. Epub 2012 Nov 24. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23179856 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding phosphatidyl inositol-specific phospholipase C from Trypanosoma cruzi.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1999 Aug 20;102(2):283-95. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(99)00108-5. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1999. PMID: 10498184
-
The IP3 receptor and Ca2+ signaling in trypanosomes.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021 Apr;1868(4):118947. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2021.118947. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 33421534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbial inositol polyphosphate metabolic pathway as drug development target.Adv Biol Regul. 2018 Jan;67:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Adv Biol Regul. 2018. PMID: 28964726 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
