Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of belimumab and telitacicept in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a retrospective, observational study
- PMID: 40172681
- PMCID: PMC11965181
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-025-01640-z
Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of belimumab and telitacicept in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a retrospective, observational study
Abstract
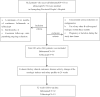
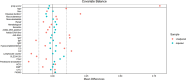
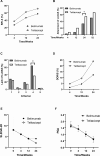
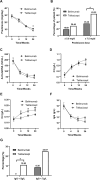
This investigation aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of belimumab and telitacicept in active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to explore potential predictors within a treat-to-target paradigm. 101 individuals were retrospectively enrolled at Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital between January 2021 and December 2023, receiving either belimumab (n = 50) or telitacicept (n = 51) in conjunction with standard therapy for more than 24 weeks. Key clinical endpoints were evaluated, with lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) as the primary outcome. Multivariate analysis was employed to investigate factors associated with failure to attain LLDAS. Baseline characteristics were balanced in both groups after propensity score-based inverse probability of treatment weighting. At 24 weeks, the rates of attainment of LLDAS were 54.86% in the telitacicept group and 33.13% in patients receiving belimumab (p = 0.048). A larger proportion of patients receiving telitacicept attained prednisone dosages of ≤ 7.5 mg/day (p = 0.012). Improvements in complement C4 levels and the occurrence of severe hypogammaglobulinemia were more pronounced among patients receiving telitacicept, with no differences in SLE Responder Index 4, DORIS remission, and renal response. Treatment with telitacicept (OR = 0.80, p = 0.032) and elevated levels of complement C3 (OR = 0.63, p = 0.003) were associated with a decreased risk of failing to achieve LLDAS. No severe adverse events were documented in both groups. Both belimumab and telitacicept displayed satisfactory effectiveness and safety profiles. Our findings imply telitacicept may offer potential benefits associated with the early attainment of LLDAS and reduced glucocorticoid exposure. Restricted by the observational design, the findings require further validation in prospective studies.
Keywords: Belimumab; IPTW; LLDAS; Systemic lupus erythematosus; Telitacicept.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences (ID: S2024-170-02). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancing systemic lupus erythematosus treatment outcomes with an early initiation of belimumab: insights from a multicenter retrospective study within the first five years.Arthritis Res Ther. 2025 May 29;27(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s13075-025-03581-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40442811 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency and predictors for early-achieved lupus low disease activity state in systemic lupus erythematosus patients treated with telitacicept or belimumab: A real-life, single-center observational study.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 14;15:1423035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423035. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38947321 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of different recommended doses of telitacicept in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 10;15:1472292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1472292. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39867893 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Bayesian statistics to support approval of intravenous belimumab in children with systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States.Lupus. 2025 Aug;34(9):943-952. doi: 10.1177/09612033251349930. Epub 2025 Jun 27. Lupus. 2025. PMID: 40577570
References
-
- Durcan L, O’Dwyer T, Petri M. Management strategies and future directions for systemic lupus erythematosus in adults. Lancet. 2019;393(10188):2332–43. - PubMed
-
- Vincent FB, Morand EF, Schneider P, Mackay F. The BAFF/APRIL system in SLE pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(6):365–73. - PubMed
-
- Arbitman L, Furie R, Vashistha H. B cell-targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. 2022;132: 102873. - PubMed
-
- Navarra SV, Guzmán RM, Gallacher AE, et al. Efficacy and safety of belimumab in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2011;377(9767):721–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

