Comprehensive genomic and transcriptomic analysis enables molecularly guided therapy options in peritoneal and pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 40174508
- PMCID: PMC11999262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.104532
Comprehensive genomic and transcriptomic analysis enables molecularly guided therapy options in peritoneal and pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Introduction: Peritoneal, pericardial and pleural mesothelioma (PeM/PcM/PM) are rare and aggressive diseases with limited survival. Molecularly guided therapy is currently not part of standard care.
Methods: This study integrates molecular and clinical data from 51 patients (among them 28 PM, one PcM, 21 PeM and one synchronous PeM/PM) enrolled in the National Center for Tumor Diseases and the German Cancer Consortium (NCT/DKTK) Molecularly Aided Stratification for Tumor Eradication Research (MASTER), a multicenter precision oncology registry trial addressing adults with rare advanced-stage cancers. Analysis comprised both somatic and germline whole exome sequencing/whole genome sequencing and transcriptome analysis leading to personalized treatment recommendations issued by a dedicated molecular tumor board. To assess clinical efficacy, progression-free survival (PFS) ratios comparing molecularly informed therapies (PFS2) to preceding systemic therapies (PFS1) were calculated. Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition applied during the observation period was assessed accordingly.
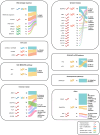
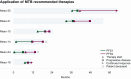
Results: Cancer-related genes altered in more than 5 out of 44 assessable patients were BAP1, CDKN2A, NF2, SETD2 and TP53. Somatic (n = 23) or germline (n = 9) alterations in homologous recombination-related genes were detected in 27/44 patients. In 21/44 cases, they were supported by positive combined homologous recombination deficiency scores or BRCAness signature. Following American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics guidelines, (likely) pathogenic germline variants in autosomal dominant cancer predisposition genes were found in 8/51 patients. Molecular tumor board recommendations were issued in 46 cases and applied in 6 cases. Mean PFS ratio was 2.45 (n = 5). Median PFS2 was 6.5 months (n = 6), median PFS1 was 4.0 months (n = 5). A total of 27 patients received immune checkpoint inhibition during the observation period leading to a mean PFS ratio of 1.69 (n = 19).
Conclusions: In mesothelioma, comprehensive molecular analysis can provide valuable clinically actionable information. Molecularly informed therapy recommendations can lead to clinical benefit.
Keywords: Key words: precision oncology; homologous repair deficiency; peritoneal mesothelioma; pleural mesothelioma; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Raptopoulos V. Peritoneal mesothelioma. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 1985;24(4):293–328. - PubMed
-
- Larson T., Melnikova N., Davis S.I., Jamison P. Incidence and descriptive epidemiology of mesothelioma in the United States, 1999-2002. Int J Occup Environ Health. 2007;13(4):398–403. - PubMed
-
- Moolgavkar S.H., Meza R., Turim J. Pleural and peritoneal mesotheliomas in SEER: age effects and temporal trends, 1973-2005. Cancer Causes Control. 2009;20(6):935–944. - PubMed
-
- Baumann F., Ambrosi J.P., Carbone M. Asbestos is not just asbestos: an unrecognised health hazard. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(7):576–578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

