Incretins and SGLT-2 inhibitors in diabetic patients with neuroendocrine tumors: current updates and future directions
- PMID: 40175622
- PMCID: PMC12316766
- DOI: 10.1007/s11154-025-09958-5
Incretins and SGLT-2 inhibitors in diabetic patients with neuroendocrine tumors: current updates and future directions
Abstract
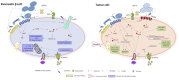
Neuroendocrine tumors (NET) are frequently associated with glycemic disorders, such as prediabetes or diabetes, which may result from either surgical or medical treatments or hormonal hypersecretion by the tumor itself. Moreover, pre-existing diabetes is a known risk factor for NET development, with metabolic control and antidiabetic therapies potentially influencing tumor progression. The complex interplay between diabetes and NET, which share several molecular pathways, has spurred interest in the anti-cancer effects of antidiabetic medications. This is particularly relevant as new antidiabetic drugs continue to emerge, including sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and incretin-based therapies, such as dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists and dual GIP/GLP- 1 R agonists. This review explores the impact of these novel pharmacological options on NET development and progression through a comprehensive analysis of pre-clinical and clinical studies, with the purpose to evaluate safety and feasibility of introducing these drugs in the treatment of NETs patients. We conducted a comprehensive search of online databases, including PubMed, ISI Web of Science, and Scopus, for studies assessing the therapeutic effects and potential mechanisms of action of incretins and SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with NET. These novel antidiabetic drugs exhibit promising anticancer properties, potentially inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis, though concerns about certain cancer risks remain. Based on current evidence, the benefits of incretin-based therapies outweigh any potential cancer risks, leading to the proposal of tailored management algorithms for diabetes in NET patients, factoring in the diabetes aetiology, comorbidities, and life expectancy.
Keywords: Diabetes; Dual GIP/GLP-1R agonists; GLP-1R agonists–DPP-4 inhibitors; Neuroendocrine tumors; SGLT-2 inhibitors.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Associazione Italiana di Oncologia Medica (AIOM). Linee guida per la diagnosi e il trattamento delle neoplasie neuroendocrine(Rapporto n. 311). 2021. https://www.iss.it/documents/20126/8403839/LG-311-Neoplasie-Neuroendocri...
-
- Vergès B, Cariou B. mTOR inhibitors and diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2015;110:101–8. 10.1016/j.diabres.2015.09.014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

