Advancing Obesity Management: the Very Low-Energy Ketogenic therapy (VLEKT) as an Evolution of the "Traditional" Ketogenic Diet
- PMID: 40175850
- PMCID: PMC11965229
- DOI: 10.1007/s13679-025-00622-2
Advancing Obesity Management: the Very Low-Energy Ketogenic therapy (VLEKT) as an Evolution of the "Traditional" Ketogenic Diet
Abstract
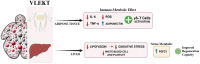
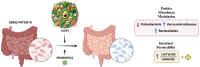
Purpose of review: This narrative review comprehensively analyzes VLEKT as an advanced nutritional strategy for obesity management. The focus is on the beneficial effects on key disease organs, such as adipose tissue and liver, as well as the modulation of intestinal permeability and its fundamental role in influencing the gut microbiota and inflammatory pathways.
Recent findings: The impact of VLEKT on obesity-related comorbidities, including metabolic syndrome, cardiovascular disease, endocrine disorders, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), neurological disorders, and kidney alterations, is also investigated. Moreover, to assess its wider application in obesity treatment, the combination of ketogenic regimes with additional strategies such as physical activity, bariatric surgery, and digital health technologies is examined. Despite promising clinical results, adherence to VLEKT and potential nutritional deficiencies require careful follow-up and individualized programming monitored by specialists. Future research should focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying the effects on physiological systems, and long-term safety. Nevertheless, VLEKT is an innovative approach to obesity treatment, offering a target-oriented and highly effective strategy for people fighting against overweight and its associated medical complications. Obesity is a multifactorial and chronic disease associated with numerous comorbidities; given its increasing prevalence, effective and personalized intervention strategies are crucial to inhibit the "obesity pandemic" according to a "food re-educational" protocol. Among dietary interventions, the ketogenic diet (KD) has attracted attention for its effectiveness in weight management and metabolic benefits. A variant, the very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD), more recently defined as very low-energy ketogenic diet (VLEKD), combines the metabolic benefits of ketosis with substantial calorie restriction, improving overall health.
Keywords: Ketogenic diet (KD); MASLD; Obesity; Obesity metabolism; Very low calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD); Very low-energy ketogenic therapy (VLEKT).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Safaei M, Sundararajan EA, Driss M, Boulila W, Shapi’i A. A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Comput Biol Med. 2021;136:104754. - PubMed
-
- Canuto R, Garcez A, de Souza RV, Kac G, Olinto MTA. Nutritional intervention strategies for the management of overweight and obesity in primary health care: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2021;22:e13143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

