The effectiveness of fasting regimens on serum levels of some major weight regulating hormones: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis in randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40176106
- PMCID: PMC11966850
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-025-00834-1
The effectiveness of fasting regimens on serum levels of some major weight regulating hormones: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and meta-analysis in randomized controlled trial
Abstract
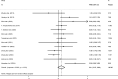
A current investigation was performed to review and summarize the results of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) studies that have assessed the effectiveness of fasting regimens (FRs) including intermittent fasting (IF), time-restricted feeding (TRF), alternate day fasting (ADF) and fasting-mimicking diet (FMD) on some weight regulation hormones included; leptin, adiponectin, ghrelin, and resistin in healthy, overweight and obese adults recently. Four databases have been reviewed until June 2024 using keywords related to the subject of the study. Overall, 16 documents were considered in this study. Based on Pooled effect sizes, the FRs marginal significantly increased the level of adiponectin (weighted mean differences (WMD): 0.41 µg/ml, 95% confidence interval (CI): - 0.07 to 0.89, P: 0.09) and also significantly decreased the level of leptin (WMD: - 2.65 ng/ml, 95% CI: - 3.86 to - 1.44, p < 0.001) and ghrelin (WMD: - 0.57 ng/ml, 95% CI: - 1.01 to - 0.03, P: 0.01). There was no significant effect of this regimen approach on resistin levels. In general, according to this evaluation, FRs have a beneficial impact on weight-regulating hormone levels, still the long-term effects of these dietary approaches should also be evaluated in future studies.
Keywords: Fasting regimen; Hormone; Meta-analysis; Obesity.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics, consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The effects of separate and combined dietary weight loss and exercise on fasting ghrelin concentrations in overweight and obese women: a randomized controlled trial.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015 Mar;82(3):369-76. doi: 10.1111/cen.12483. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 24796864 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The influence of fasting and energy-restricted diets on leptin and adiponectin levels in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr. 2021 Apr;40(4):1811-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.034. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33158587
-
Green Tea Extract and Catechol-O-Methyltransferase Genotype Modify Fasting Serum Insulin and Plasma Adiponectin Concentrations in a Randomized Controlled Trial of Overweight and Obese Postmenopausal Women.J Nutr. 2016 Jan;146(1):38-45. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.222414. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 26581683 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of diurnal intermittent fasting during Ramadan on ghrelin, leptin, melatonin, and cortisol levels among overweight and obese subjects: A prospective observational study.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 26;15(8):e0237922. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237922. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32845924 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on leptin and adiponectin: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Hormones (Athens). 2021 Jun;20(2):237-246. doi: 10.1007/s42000-021-00285-3. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Hormones (Athens). 2021. PMID: 33786736
Cited by
-
Effects of 4:3 Intermittent Fasting on Eating Behaviors and Appetite Hormones: A Secondary Analysis of a 12-Month Behavioral Weight Loss Intervention.Nutrients. 2025 Jul 21;17(14):2385. doi: 10.3390/nu17142385. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40733010 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity, 2023. Accessed 3 September 2023.Available from https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 [
-
- World Obesity Federation. World obesity atlas 2024. Accessed March 2024. Available from https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/WOF-Obesity-Atlas-v7.pdf [
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and overweight. www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight/ (accessed prior to 7 March 2024).
-
- Muñoz-Hernández L, Márquez-López Z, Mehta R, Aguilar-Salinas CA. Intermittent fasting as part of the management for T2DM: from animal models to human clinical studies. Curr DiabRep. 2020;20:1–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

