Parental kynurenine 3-monooxygenase genotype in mice directs sex-specific behavioral outcomes in offspring
- PMID: 40176166
- PMCID: PMC11967062
- DOI: 10.1186/s13293-025-00703-w
Parental kynurenine 3-monooxygenase genotype in mice directs sex-specific behavioral outcomes in offspring
Abstract
Background: Disruptions in brain development can impact behavioral traits and increase the risk of neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder, often in sex-specific ways. Dysregulation of the kynurenine pathway (KP) of tryptophan metabolism has been implicated in cognitive and neurodevelopmental disorders. Increased brain kynurenic acid (KYNA), a neuroactive metabolite implicated in cognition and sleep homeostasis, and variations in the Kmo gene, which encodes kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO), have been identified in these patients. We hypothesize that parental Kmo genetics influence KP biochemistry, sleep behavior and brain energy demands, contributing to impairments in cognition and sleep in offspring through the influence of parental genotype and genetic nurture mechanisms.
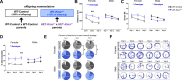
Methods: A mouse model of partial Kmo deficiency, Kmo heterozygous (HET-Kmo+/-), was used to examine brain KMO activity, KYNA levels, and sleep behavior in HET-Kmo+/- compared to wild-type control (WT-Control) mice. Brain mitochondrial respiration was assessed, and KP metabolites and corticosterone levels were measured in breast milk. Behavioral assessments were conducted on wild-type offspring from two parental groups: (i) WT-Control from WT-Control parents, (ii) wild-type Kmo (WT-Kmo+/+) from Kmo heterozygous parents (HET-Kmo+/-). All mice were C57Bl/6J background strain. Adult female and male offspring underwent behavioral testing for learning, memory, anxiety-like behavior and sleep-wake patterns.
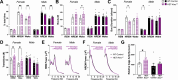
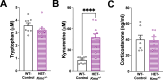
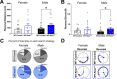
Results: HET-Kmo+/- mice exhibited reduced brain KMO activity, increased KYNA levels, and disrupted sleep architecture and electroencephalogram (EEG) power spectra. Mitochondrial respiration (Complex I and Complex II activity) and electron transport chain protein levels were impaired in the hippocampus of HET-Kmo+/- females. Breast milk from HET-Kmo+/- mothers increased kynurenine exposure during lactation but corticosterone levels were unchanged. Compared to WT-Control offspring, WT-Kmo+/+ females showed impaired spatial learning, heightened anxiety, reduced sleep and abnormal EEG spectral power. WT-Kmo+/+ males had deficits in reversal learning but no sleep disturbances or anxiety-like behaviors.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that Kmo deficiency impacts KP biochemistry, sleep behavior, and brain mitochondrial function. Even though WT-Kmo+/+ inherit identical genetic material as WT-Control, their development might be shaped by the parent's physiology, behavior, or metabolic state influenced by their Kmo genotype, leading to phenotypic sex-specific differences in offspring.
Keywords: Cognition; Kynurenine pathway; Neurodevelopment; Parental genotype; Sleep.
Plain language summary
Interactions between genetic and environmental factors are carefully regulated during the intricate process of brain development. While genetic information is directly inherited from parents, emerging evidence suggests that parental genetic factors can also shape the environment influencing children’s development in a sex-specific ways. Disruptions in brain development can impact cognitive and behavioral traits and increase the risk of neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder. This study explored how kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (Kmo) genotype affects female and male mice, focusing on potential sex-specific behavioral changes in offspring born to parents with a genetic disruption in Kmo. We found that female and male mice with partial Kmo deficiency experienced reduced sleep and increased sleep pressure. In female mice, Kmo deficiency impaired mitochondrial energy production in the brain. We also observed alterations in tryptophan metabolism and nutrient composition in the breast milk of Kmo-deficient females. In adult offspring born to Kmo-deficient parents, females exhibited learning difficulties, heightened anxiety-like behaviors, and sleep disturbances. In contrast, male offspring showed mild cognitive impairments but no major sleep issues. These findings highlight that parental Kmo genotype can influence sex differences in cognitive and sleep-related behaviors in offspring. This underscores the importance of considering parental genetic factors when studying neurodevelopmental disorders and associated behavioral outcomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: No applicable. Consent for publication: All authors consent to publication of the work. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Lee SH, Ripke S, Neale BM, Faraone SV, Purcell SM, Perlis RH, Mowry BJ, Thapar A, Goddard ME, Witte JS, Absher D, Agartz I, Akil H, Amin F, Andreassen OA, Anjorin A, Anney R, Anttila V, Arking DE, Asherson P, Azevedo MH, Backlund L, Badner JA, Bailey AJ, Banaschewski T, Barchas JD, Barnes MR, Barrett TB, Bass N, Battaglia A, Bauer M, Bayés M, Bellivier F, Bergen SE, Berrettini W, Betancur C, Bettecken T, Biederman J, Binder EB, Black DW, Blackwood DH, Bloss CS, Boehnke M, Boomsma DI, Breen G, Breuer R, Bruggeman R, Cormican P, Buccola NG, Buitelaar JK, Bunney WE, Buxbaum JD, Byerley WF, Byrne EM, Caesar S, Cahn W, Cantor RM, Casas M, Chakravarti A, Chambert K, Choudhury K, Cichon S, Cloninger CR, Collier DA, Cook EH, Coon H, Cormand B, Corvin A, Coryell WH, Craig DW, Craig IW, Crosbie J, Cuccaro ML, Curtis D, Czamara D, Datta S, Dawson G, Day R, De Geus EJ, Degenhardt F, Djurovic S, Donohoe GJ, Doyle AE, Duan J, Dudbridge F, Duketis E, Ebstein RP, Edenberg HJ, Elia J, Ennis S, Etain B, Fanous A, Farmer AE, Ferrier IN, Flickinger M, Fombonne E, Foroud T, Frank J, Franke B, Fraser C, Freedman R, Freimer NB, Freitag CM, Friedl M, Frisén L, Gallagher L, Gejman PV, Georgieva L, Gershon ES, Geschwind DH, Giegling I, Gill M, Gordon SD, Gordon-Smith K, Green EK, Greenwood TA, Grice DE, Gross M, Grozeva D, Guan W, Gurling H, De Haan L, Haines JL, Hakonarson H, Hallmayer J, Hamilton SP, Hamshere ML, Hansen TF, Hartmann AM, Hautzinger M, Heath AC, Henders AK, Herms S, Hickie IB, Hipolito M, Hoefels S, Holmans PA, Holsboer F, Hoogendijk WJ, Hottenga JJ, Hultman CM, Hus V, Ingason A, Ising M, Jamain S, Jones EG, Jones I, Jones L, Tzeng JY, Kähler AK, Kahn RS, Kandaswamy R, Keller MC, Kennedy JL, Kenny E, Kent L, Kim Y, Kirov GK, Klauck SM, Klei L, Knowles JA, Kohli MA, Koller DL, Konte B, Korszun A, Krabbendam L, Krasucki R, Kuntsi J, Kwan P, Landén M, Långström N, Lathrop M, Lawrence J, Lawson WB, Leboyer M, Ledbetter DH, Lee PH, Lencz T, Lesch KP, Levinson DF, Lewis CM, Li J, Lichtenstein P, Lieberman JA, Lin DY, Linszen DH, Liu C, Lohoff FW, Loo SK, Lord C, Lowe JK, Lucae S, MacIntyre DJ, Madden PA, Maestrini E, Magnusson PK, Mahon PB, Maier W, Malhotra AK, Mane SM, Martin CL, Martin NG, Mattheisen M, Matthews K, Mattingsdal M, McCarroll SA, McGhee KA, McGough JJ, McGrath PJ, McGuffin P, McInnis MG, McIntosh A, McKinney R, McLean AW, McMahon FJ, McMahon WM, McQuillin A, Medeiros H, Medland SE, Meier S, Melle I, Meng F, Meyer J, Middeldorp CM, Middleton L, Milanova V, Miranda A, Monaco AP, Montgomery GW, Moran JL, Moreno-De-Luca D, Morken G, Morris DW, Morrow EM, Moskvina V, Muglia P, Mühleisen TW, Muir WJ, Müller-Myhsok B, Murtha M, Myers RM, Myin-Germeys I, Neale MC, Nelson SF, Nievergelt CM, Nikolov I, Nimgaonkar V, Nolen WA, Nöthen MM, Nurnberger JI, Nwulia EA, Nyholt DR, O'Dushlaine C, Oades RD, Olincy A, Oliveira G, Olsen L, Ophoff RA, Osby U, Owen MJ, Palotie A, Parr JR, Paterson AD, Pato CN, Pato MT, Penninx BW, Pergadia ML, Pericak-Vance MA, Pickard BS, Pimm J, Piven J, Posthuma D, Potash JB, Poustka F, Propping P, Puri V, Quested DJ, Quinn EM, Ramos-Quiroga JA, Rasmussen HB, Raychaudhuri S, Rehnström K, Reif A, Ribasés M, Rice JP, Rietschel M, Roeder K, Roeyers H, Rossin L, Rothenberger A, Rouleau G, Ruderfer D, Rujescu D, Sanders AR, Sanders SJ, Santangelo SL, Sergeant JA, Schachar R, Schalling M, Schatzberg AF, Scheftner WA, Schellenberg GD, Scherer SW, Schork NJ, Schulze TG, Schumacher J, Schwarz M, Scolnick E, Scott LJ, Shi J, Shilling PD, Shyn SI, Silverman JM, Slager SL, Smalley SL, Smit JH, Smith EN, Sonuga-Barke EJ, St Clair D, State M, Steffens M, Steinhausen HC, Strauss JS, Strohmaier J, Stroup TS, Sutcliffe JS, Szatmari P, Szelinger S, Thirumalai S, Thompson RC, Todorov AA, Tozzi F, Treutlein J, Uhr M, van den Oord EJ, Van Grootheest G, Van Os J, Vicente AM, Vieland VJ, Vincent JB, Visscher PM, Walsh CA, Wassink TH, Watson SJ, Weissman MM, Werge T, Wienker TF, Wijsman EM, Willemsen G, Williams N, Willsey AJ, Witt SH, Xu W, Young AH, Yu TW, Zammit S, Zandi PP, Zhang P, Zitman FG, Zöllner S, Devlin B, Kelsoe JR, Sklar P, Daly MJ, O'Donovan MC, Craddock N, Sullivan PF, Smoller JW, Kendler KS, Wray NR; International Inflammatory Bowel Disease Genetics Consortium (IIBDGC). Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat Genet. 2013;45:9:984–94. 10.1038/ng.2711. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

