Transdermal administration of herbal essential oil alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating metabolism and gut microbiota
- PMID: 40176906
- PMCID: PMC11962428
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565030
Transdermal administration of herbal essential oil alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating metabolism and gut microbiota
Erratum in
-
Correction: Transdermal administration of herbal essential oil alleviates high-fat diet-induced obesity by regulating metabolism and gut microbiota.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Dec 5;16:1743063. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1743063. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 41424787 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: Obesity, a global health challenge, is characterized by excessive fat accumulation and associated metabolic disorders. The ZhiZhu decoction, a traditional Chinese herbal formula consisting of Citrus aurantium L. (ZS, ZhiShi in Chinese) and Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz (BZ, Baizhu in Chinese), is widely recognized in clinics for its gastrointestinal regulatory effects.
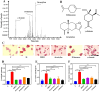
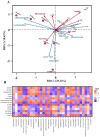
Methods: The chemical composition of ZS-BZ essential oil (ZBEO) was characterized using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Concurrently, we conducted in vitro investigations using HepG2 hepatoma cells to evaluate its anti-lipid deposition potential. To further elucidate the anti-obesity mechanisms, an in vivo model was established through high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obese rats, followed by transdermal ZBEO administration. Systemic analyses were performed integrating serum metabolomic profiling via UPLC-QTOF-MS and gut microbiota dynamics assessment through 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
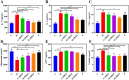
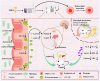
Results: ZBEO, rich in atractylon, D-limonene, and γ-elemene and shown to reduce lipid accumulation. Transdermal ZBEO administration in obese rats led to significant weight loss and improved serum metabolic indexes related to the POMC/CART signaling pathway. Additionally, ZBEO altered gut microbiota, enhancing beneficial bacteria and affecting metabolic pathways linked to obesity.
Discussion: We discovered that ZBEO exerts a significant influence on obesity by modulating key biological processes, including glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and the composition of gut microbiota.
Keywords: essential oil; gut microbiota; inflammation; lipid mechanism; obesity.
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Yang, Yang, Lin, Liu, Li, Yan, Luo, Qin and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




References
-
- Alanazi S. M., Alsaqer R. A., Alsaeed F. I., Almakhaytah R. M., Buwashl N. T., Mohamed M. E., et al. (2023). Studying the actions of sage and thymoquinone combination on metabolic syndrome induced by high-fat diet in rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 27 (6), 2404–2418. 10.26355/eurrev_202303_31775 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

