Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced pancreatitis: a systematic review and real-world pharmacovigilance analysis
- PMID: 40176908
- PMCID: PMC11962026
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1426847
Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced pancreatitis: a systematic review and real-world pharmacovigilance analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Immune checkpoint inhibitors-induced pancreatitis (ICIs-P) is an uncommon immune-related adverse event. The available evidence consists mostly of case reports, case series, and narrative reviews. This research focuses on the clinical characteristics and management options for ICIs-P to provide a practice-based global perspective on this disease.
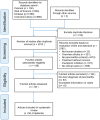
Methods: Five electronic databases were systematically reviewed to identify the relevant studies. Furthermore, we performed a disproportionality analysis utilizing OpenVigil 2.1 to interrogate the United States Food and Drug Administration's Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database.
Results: A total of 61 patients from 58 studies were included in this study. Most patients with ICIs-P were males (60.7%). Most patients received anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy (78.7%) or anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monotherapy in conjunction with CTLA-4 blockade (19.7%). The median time from the initiation of immune checkpoint inhibitors treatment to pancreatitis was 108 days (range 52-278). Most cases were severe or life-threatening (G3-G4; 64.0%). Corticosteroids were administered to 73.8% of the patients during the treatment of pancreatitis. Regarding treatment outcomes, ICIs-P was reversible in most cases (83.6%), despite the 8.2% relapse and 8.2% deaths. We identified 606 reports of pancreatitis associated with ICIs in the FAERS database, with the greatest proportion of males (50.7%), 62.0% of PD-1 inhibitors, and 22.1% of all reports of death or life-threatening outcomes. Signals indicating pancreatitis were observed across all ICIs, with particular emphasis on Cemiplimab, Pembrolizumab and Nivolumab.
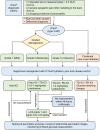
Conclusion: By using a pharmacovigilance database, we discovered an elevated risk of pancreatitis following ICIs therapy, especially with PD-1 inhibitors. Meanwhile, risk factors for ICIs-P remain poorly understood, and diagnosis is challenging. Which may manifest as asymptomatic elevated pancreatic enzyme levels or clinical pancreatitis. Patients with pancreatitis symptoms should have their lipase and amylase levels and radiology evaluated. Diagnosis should be made by excluding other causes. Steroids are the cornerstone of ICIs-P treatment and slow dose reduction is recommended to reduce recurrence.
Keywords: immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune-related adverse event; immunotherapy; pancreatitis; pharmacovigilance analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Fang, Wang, Zhang, Zhu, Yan and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alessandrino F., Sahu S., Nishino M., Adeni A. E., Tirumani S. H., Shinagare A. B., et al. (2019). Frequency and imaging features of abdominal immune-related adverse events in metastatic lung cancer patients treated with PD-1 inhibitor. Abdom. Radiol. (NY) 44 (5), 1917–1927. 10.1007/s00261-019-01935-2 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bachiller M. D., Piernavieja L. C., Chico P. T., et al. (2020). Pancreatitis induced by immunotherapy? Two case reports. Eur. J. Hosp. Pharm. 27 (Suppl. 1), A167–A168. 10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-eahpconf.356 - DOI
-
- Bai X., Jiang S., Zhou Y., Zhen H., Ji J., Li Y., et al. (2021). Common immune-related adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors in the gastrointestinal system: a study based on the us Food and drug administration adverse event reporting system. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 720776. 10.3389/fphar.2021.720776 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

