The revolutionary role of placental derivatives in biomedical research
- PMID: 40177109
- PMCID: PMC11964572
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.03.011
The revolutionary role of placental derivatives in biomedical research
Abstract
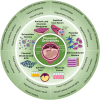
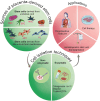
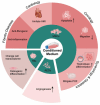
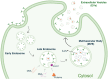
The human placenta is a transient yet crucial organ that plays a key role in sustaining the relationship between the maternal and fetal organisms. Despite its historical classification as "biowaste," placental tissues have garnered increasing attention since the early 1900s for their significant medical potential, particularly in wound repair and surgical application. As ethical considerations regarding human placental derivatives have largely been assuaged in many countries, they have gained significant attention due to their versatile applications in various biomedical fields, such as biomedical engineering, regenerative medicine, and pharmacology. Moreover, there is a substantial trend toward various animal product substitutions in laboratory research with human placental derivatives, reflecting a broader commitment to advancing ethical and sustainable research methodologies. This review provides a comprehensive examination of the current applications of human placental derivatives, explores the mechanisms behind their therapeutic effects, and outlines the future potential and directions of this rapidly advancing field.
Keywords: Biomedical research; Decellularization; Extracellular matrix; Extracellular vesicle; Placenta; Regenerative medicine; Stem cells.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Saeid Moghassemi reports financial support was provided by Fund for Scientific Research. Christiani Andrade Amorim reports a relationship with Foundation Against Cancer that includes: funding grants. Christiani Andrade Amorim reports a relationship with Fund for Scientific Research that includes: funding grants. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Najafi-Ghalehlou N., Feizkhah A., Mobayen M., Pourmohammadi-Bejarpasi Z., Shekarchi S., Roushandeh A.M., Roudkenar M.H. Plumping up a cushion of human biowaste in regenerative medicine: novel insights into a state-of-the-art reserve arsenal. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports. 2022;18(8):2709–2739. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis J. Skin transplantation with a review of 550 cases at the johns hopkins hospital. Johns Hopkins Med. J. 1910;15(307):307–398.
-
- Gujjar S., Tyagi A., Sainger S., Bharti P., Nain V., Sood P., Jayabal P., Sharma J.C., Sharma P., Rajput S. Biocompatible human placental extracellular matrix derived hydrogels. Advanced Biology. 2024;8(1) - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

