Cardiac Troponin I Biosensors: Innovations in Real-Time Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 40177114
- PMCID: PMC11961551
- DOI: 10.1002/ansa.70009
Cardiac Troponin I Biosensors: Innovations in Real-Time Diagnosis of Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
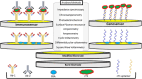
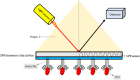
Cardiac troponin I (cTnI) is a crucial biological macromolecule found in the contractile apparatus of cardiac myocytes, exclusively expressed in cardiomyocytes. It is released into the bloodstream upon cardiac tissue injury, serving as a vital biomarker for the early detection of various heart diseases. Despite advancements in cTnI diagnostics and cardiovascular disease (CVD) detection, there is an ongoing need for more effective early diagnostic methods and innovative approaches. Current CVD diagnosis often relies on clinical signs and symptoms, supplemented by molecular imaging (MI) or biomarkers associated with CVD. However, challenges remain regarding the reliability, specificity and accuracy of analyses for myocardial infarction, particularly in its early stages. Emerging nanomaterial systems present promising solutions for enhancing diagnostic tools due to their unique physical and chemical properties. Various nanomaterials, such as gold nanoparticles, carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, lipids and polymer nanoparticles, are paving new pathways for cardiac disease detection. The advancements in nanomaterial science offer exciting opportunities for cardiac screening. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these advancements, categorizing research efforts focused on both optical and electrochemical platforms, thereby contributing to the evolution of cardiac screening methodologies and addressing the critical need for reliable early diagnostic solutions.
Keywords: biomedical engineering; biosensors; cardiac troponin I (cTnI); cardiovascular diseases (CVDs); nanodiagnoses.
© 2025 The Author(s). Analytical Science Advances published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nanomaterial-based biosensors and immunosensors for quantitative determination of cardiac troponins.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Sep 10;159:425-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.07.031. Epub 2018 Jul 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 30041152 Review.
-
Graphene Quantum Dots-Based Electrochemical Biosensing Platform for Early Detection of Acute Myocardial Infarction.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;12(2):77. doi: 10.3390/bios12020077. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35200338 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticle biosensors for cardiovascular disease detection.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 Feb 1;567:120094. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.120094. Epub 2024 Dec 15. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39681229 Review.
-
Clinical relevance and advances in detection of translational biomarker cardiac troponin.Anal Biochem. 2024 Jun;689:115505. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2024.115505. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Anal Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38460900 Review.
-
Electrochemical cardiovascular platforms: Current state of the art and beyond.Biosens Bioelectron. 2019 Apr 15;131:287-298. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2019.02.010. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2019. PMID: 30851492 Review.
References
-
- Bakirhan N. K., Ozcelikay G., and Ozkan S. A., “Recent Progress on the Sensitive Detection of Cardiovascular Disease Markers by Electrochemical‐based Biosensors,” Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 159 (2018): 406–424. - PubMed
-
- Han X., Li S., Peng Z., Othman A. M., and Leblanc R., “Recent Development of Cardiac Troponin I Detection,” ACS Sensors 1, no. 2 (2016): 106–114.
-
- Sridhar C., Lih O. S., Jahmunah V., et al., “Accurate Detection of Myocardial Infarction Using Non Linear Features With ECG Signals,” Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing 12, no. 3 (2021): 3227–3244.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
