A dual-functional nanogold tablet as a plasmonic and nanozyme sensor for point-of-care applications
- PMID: 40177386
- PMCID: PMC11960780
- DOI: 10.1039/d5na00082c
A dual-functional nanogold tablet as a plasmonic and nanozyme sensor for point-of-care applications
Abstract
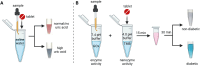
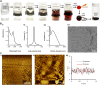
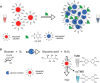
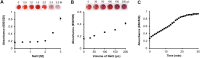
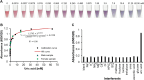
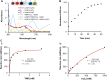
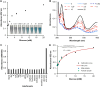
Point-of-care (POC) devices provide on-site disease diagnosis, particularly in resource-limited settings. Despite considerable progress in POC testing, the availability of commercial devices remains limited, primarily due to challenges in detection sensitivity and portability. Furthermore, advancements in existing POC devices are essential to better meet the needs of end-users. Herein, we present a colorimetric dual-functional tablet sensor using dextran-gold nanoparticles (dAuNPs) to detect and quantify uric acid and glucose levels in urine. Our tablet sensor combines the plasmonic and nanozyme properties of dAuNPs, resulting in highly sensitive detection of both biomarkers. Interestingly, we fabricated the nanogold tablet directly from the dAuNP solution without the addition of any external stabilizer or tablet-forming reagent, thus naming it a direct tablet. An enzyme-free approach was employed for uric acid detection, providing a wide detection range of 0.00187-7.8 mM and a low detection limit of 0.0037 mM, attributed to the hydrogen bonding between dextran and uric acid. On the other hand, the unique nanozyme properties of dAuNPs exhibited exclusive POx-mimetic activity for glucose detection (K m = 0.106 mM and V max = 369.72 mM min-1), with a lower detection limit of 0.625 mM. Our dual-functional tablet offers exceptional substrate selectivity for the colorimetric-chromogenic assay of both uric acid and glucose. This dual-functionality not only provides a highly sensitive, selective, and cost-effective detection strategy for resource-limited settings but also introduces a new avenue for designing customizable plasmonic-nanozyme nanogold tablet sensors as a powerful tool for rapid diagnosis.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tailoring plasmonic sensing strategies for the rapid and sensitive detection of hypochlorite in swimming water samples.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Mar 7;191(4):183. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06246-y. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38451315
-
Tablet-Based Sensor: A Stable and User-Friendly Tool for Point-of-Care Detection of Glucose in Urine.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 19;13(9):893. doi: 10.3390/bios13090893. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754126 Free PMC article.
-
A portable colorimetric sensing platform for rapid and sensitive quantification of dichlorvos pesticide based on Fe-Mn bimetallic oxide nanozyme-participated highly efficient chromogenic catalysis.Anal Chim Acta. 2024 Mar 1;1292:342243. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2024.342243. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Anal Chim Acta. 2024. PMID: 38309847
-
Nanozyme-based aptasensors for the detection of tumor biomarkers.J Biol Eng. 2025 Feb 7;19(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13036-025-00485-0. J Biol Eng. 2025. PMID: 39920818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic nanomaterials with unique nanozymes-like characteristics for colorimetric sensors: A review.Talanta. 2021 Aug 1;230:122299. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122299. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 33934768 Review.
References
-
- Udugama B. Kadhiresan P. Samarakoon A. Chan W. C. W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:17341–17349. - PubMed
-
- Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. Pennings K. Leung V. Liu M. Carrasquilla C. Kannan B. Li Y. Pelton R. Brennan J. D. Filipe C. D. M. Angew. Chem. 2014;53:6155–6158. - PubMed
-
- Al-Kassawneh M. Sadiq Z. Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022;38:100526.
-
- Sadiq Z. Al-Kassawneh M. Safiabadi Tali S. H. Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. Microchim. Acta. 2024;191:183. - PubMed
-
- Esfahani A. R. R. Sadiq Z. Oyewunmi O. D. Safiabadi Tali S. H. Usen N. Boffito D. C. Jahanshahi-Anbuhi S. Analyst. 2021;146:3697–3708. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

