Comprehensive analysis of the ischemic stroke burden at global, regional, and national levels (1990-2021): trends, influencing factors, and future projections
- PMID: 40177409
- PMCID: PMC11961430
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1492691
Comprehensive analysis of the ischemic stroke burden at global, regional, and national levels (1990-2021): trends, influencing factors, and future projections
Abstract
Background and purpose: Estimating the global burden of ischemic strokes (IS) is crucial for enhancing prevention and control strategies.
Methods: We collected four epidemiological indicators-prevalence, incidence, deaths, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs)-for ischemic stroke (IS) from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) database, which covers the years 1990 to 2021. Our research analyzed the features of the IS burden and described the trends of these four indicators.
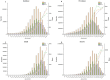
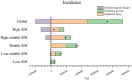
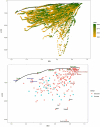
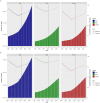
Results: The Joinpoint and age-period-cohort models reflected the changing trends in age-standardized indicators. Decomposition analysis examined the factors influencing each epidemiological indicator. The Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) model detailed changes in the number and rate of IS from 1990 to 2021 and projected trends through 2046. The Norpred model was used to verify the stability of the BAPC prediction results. The prevalence, incidence, deaths, and DALYs due to IS generally exhibited a downward trend. However, the predictions indicated that while the age-standardized incidence rate decreased from 1990 to 2015, this trend reversed between 2016 and 2021 and is expected to continue until 2046. This reversal is likely driven by factors such as population aging, given that age is a strongly correlated risk factor for IS. The IS burden was negatively associated with socio-demographic index (SDI) levels, with high systolic blood pressure identified as the largest risk factor for DALYs and deaths. The consistency between the BAPC and Norpred models enhances the reliability of these projections.
Conclusion: Over the past two decades, trends in prevalence, incidence, deaths, and DALYs have all declined. However, projections suggest that incidence will show an upward trend over the next two decades.
Keywords: Joinpoint regression; forecasting analysis; global burden of disease study; ischemic stroke; preventive health services; trends analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Lu, Jie, Chao, Zhu and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. American Heart Association Council on epidemiology and prevention statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke Statistics-2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2020) 141:e139–596. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000757, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

