Size-transformable nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy
- PMID: 40177555
- PMCID: PMC11959941
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.11.012
Size-transformable nanotherapeutics for cancer therapy
Abstract
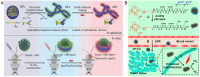
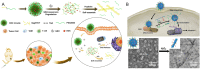
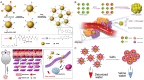
The size of nanodrugs plays a crucial role in shaping their chemical and physical characteristics, consequently influencing their therapeutic and diagnostic interactions within biological systems. The optimal size of nanomedicines, whether small or large, offers distinct advantages in disease treatment, creating a dilemma in the selection process. Addressing this challenge, size-transformable nanodrugs have surfaced as a promising solution, as they can be tailored to entail the benefits associated with both small and large nanoparticles. In this review, various strategies are summarized for constructing size-transformable nanosystems with a focus on nanotherapeutic applications in the field of biomedicine. Particularly we highlight recent research developments in cancer therapy. This review aims to inspire researchers to further develop various toolboxes for fabricating size-transformable nanomedicines for improved intervention against diverse human diseases.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Drug delivery; Self-assemble; Size-transformation; Smart nanomedicine.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Sun T., Zhang Y.S., Pang B., Hyun D.C., Yang M., Xia Y. Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53:12320–12364. - PubMed
-
- Gabizon A., Martin F.J.D. Polyethylene glycol-coated (pegylated) liposomal doxorubicin. Drugs. 1997;54:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Socinski M.A., Bondarenko I., Karaseva N.A., Makhson A.M., Vynnychenko I., Okamoto I., et al. Weekly nab-paclitaxel in combination with carboplatin versus solvent-based paclitaxel plus carboplatin as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: final results of a phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:2055–2062. - PubMed
-
- Lu Y., Aimetti A.A., Langer R., Gu Z. Bioresponsive materials. Nat Rev Mater. 2016;2
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

