Targeting mTOR in myeloid cells prevents infection-associated inflammation
- PMID: 40177636
- PMCID: PMC11964677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112163
Targeting mTOR in myeloid cells prevents infection-associated inflammation
Abstract
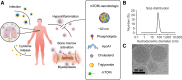
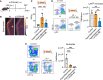
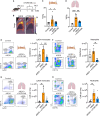
Infections, cancer, and trauma can cause life-threatening hyperinflammation. In the present study, using single-cell RNA sequencing of circulating immune cells, we found that the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway plays a critical role in myeloid cell regulation in COVID-19 patients. Previously, we developed an mTOR-inhibiting nanobiologic (mTORi-nanobiologic) that efficiently targets myeloid cells and their progenitors in the bone marrow. In vitro, we demonstrated that mTORi-nanobiologics potently inhibit infection-associated inflammation in human primary immune cells. Next, we investigated the in vivo effect of mTORi-nanobiologics in mouse models of hyperinflammation and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Using 18F-FDG uptake and flow cytometry readouts, we found mTORi-nanobiologic therapy to efficiently reduce hematopoietic organ metabolic activity and inflammation to levels comparable to those of healthy control animals. Together, we show that regulating myelopoiesis with mTORi-nanobiologics is a compelling therapeutic strategy to prevent deleterious organ inflammation in infection-related complications.
Keywords: Biochemistry; Biological sciences; Immunology; Natural sciences.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
W.J.M.M., L.A.B.J, M.N., and Z.A.F. are founders of Trained Therapeutix Discovery (TTxD). W.J.M.M is also a shareholder and CSO at the company. W.J.M.M. is founder, CTO and shareholder of BioTrip. Z.A.F. and W.J.M.M. are members of the board of TTxD. J.H.C.M.K., B.v.G., G.A.O.C., and T.J.B. are employees at TTxD. H.M.J. is a director at SyMO-Chem. S.H.M.S. and F.J.M.H. are employees at SyMO-Chem. M.S. has received unrelated research support from ArgenX N.V., Moderna, 7Hills, and Phio Pharmaceuticals. E.J.G.-B. has received honoraria from Abbott Products Operations, bioMérieux, GSK, UCB, Sobi AB and ThermoFisher Brahms GmbH, independent educational grants from Abbott Products Operations, AbbVie, bioMérieux Inc, Johnson & Johnson, InCyte, MSD, Novartis, UCB, Sanofi, and Sobi. M.M.M. is the scientific founder of Lemba Therapeutics. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article exist.
Figures


References
-
- Ikuta K.S., Swetschinski L.R., Robles Aguilar G., Sharara F., Mestrovic T., Gray A.P., Davis Weaver N., Wool E.E., Han C., Gershberg Hayoon A., et al. Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2022;400:2221–2248. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02185-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

