The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40177654
- PMCID: PMC11964182
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2024-1134
The safety and efficacy of BCG combined with mitomycin C compared with BCG monotherapy in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: We sought to determine the efficacy and safety of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) combined with mitomycin C (MMC) compared with BCG monotherapy in intravesical therapies for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
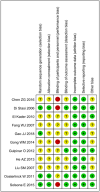
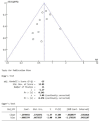
Methods: We followed the recommended PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. Systematic literatures were performed on PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CNKI, CBM, VIP, Wan Fang, and Clinical Trials.gov. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing BCG combined with MMC and BCG monotherapy in intravesical therapies for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients were searched until August 1, 2023.
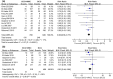
Results: This meta-analysis included 11 RCTs with a total of 1,349 subjects. Compared with BCG monotherapy, BCG combined with MMC was associated with lower disease recurrence rate (relative risk [RR] 0.66, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.56-0.77, P < 0.00001), disease progression rate (RR 0.61, 95% CI: 0.44-0.84, P = 0.003), and disease-specific mortality (RR 0.46, 95% CI: 0.26-0.78, P = 0.004). However, there was a higher incidence of systemic adverse reactions (RR 1.57, 95% CI: 1.22-2.02, P = 0.0004). There was no significant difference in the incidence of local adverse reactions (RR 1.07, 95% CI: 0.95-1.20, P = 0.26) and all-cause mortality (RR 0.80, 95% CI: 0.62-1.03, P = 0.08) between the two groups.
Conclusions: BCG combined with MMC was associated with a decreased risk of bladder cancer recurrence and disease progression compared with BCG monotherapy. However, there was no significant difference in the incidence of local adverse events and all-cause mortality between the two groups. Due to the limitations of the number and quality of the included studies, more high-quality RCTs are needed to further explore the efficacy and safety of combined therapies.
Keywords: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin; intravesical therapies; mitomycin C; non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer; urinary bladder neoplasms.
© 2025 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Sylvester RJ, Rodriguez O, Hernandez V, Turturica D, Bauerova L, Bruins HM, et al. European association of urology (EAU) prognostic factor risk groups for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) incorporating the WHO 2004/2016 and WHO 1973 classification systems for grade: An update from the EAU NMIBC guidelines panel. Eur Urol. 2021;79(4):480–8. 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.033. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sylvester RJ, Oosterlinck W, Holmang S, Sydes MR, Birtle A, Gudjonsson S, et al. Systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing a single immediate instillation of chemotherapy after transurethral resection with transurethral resection alone in patients with stage pTa-pT1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder: Which patients benefit from the instillation? Eur Urol. 2016;69(2):231–44. 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.05.050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
