Clustering of intuitive eating and psychological health identifies subgroups associated with weight loss following semaglutide
- PMID: 40177856
- PMCID: PMC12015648
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.24262
Clustering of intuitive eating and psychological health identifies subgroups associated with weight loss following semaglutide
Abstract
Objective: Obesity management requires personalized approaches. Using data from the Aviitam platform in France, this study aimed to do the following: 1) explore psychological and behavioral patterns through clustering techniques; 2) validate the robustness of these clusters; and 3) assess their association with weight-loss outcomes in severe obesity under semaglutide treatment.
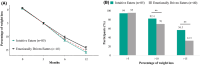
Methods: Phase 1 included 989 adults with BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2 who completed validated questionnaires, including the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and Intuitive Eating Scale-2 (IES-2). Phase 2 validated robustness in 492 individuals. Phase 3 applied clusters to 125 individuals with BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2 who were treated with semaglutide 2.4 mg/week at Montpellier University Hospital, assessing weight-loss trajectories over 12 months.
Results: The following two clusters were identified: the Intuitive Eaters Group (IEG, n = 482); and the Emotionally Driven Eaters Group (EDEG, n = 507). The IEG exhibited lower emotional distress and higher intuitive eating scores. HADS and IES-2 distinguished clusters effectively (area under the curve, 0.95). Robustness was confirmed in Phase 2. In Phase 3, the IEG demonstrated a significantly more favorable weight-loss trajectory compared to the EDEG (p = 0.03).
Conclusions: Psychological and behavioral clusters identified through HADS and IES-2 are associated with weight loss under semaglutide treatment, suggesting the value of integrating psychological and behavioral profiling into obesity care.
© 2025 The Author(s). Obesity published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Vincent Attalin and Antoine Avignon were major shareholders in Aviitam in the past 2 years, the company that developed the online platform used to collect the data. Antoine Avignon, Jean‐Baptiste Bonnet, Sarah Tournayre, and Ariane Sultan declared competing interests with Novo Nordisk A/S and Eli Lilly and Company. The other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Skinner AC, Perrin EM, Moss LA, Skelton JA. Cardiometabolic risks and severity of obesity in children and young adults. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(14):1307‐1317. - PubMed

