Administration Strategy-Dependent Mechanisms and Effects of Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles in Mouse Allergic Rhinitis Treatment
- PMID: 40179013
- PMCID: PMC11970061
- DOI: 10.1177/09636897251325673
Administration Strategy-Dependent Mechanisms and Effects of Human Adipose Tissue Stem Cell Extracellular Vesicles in Mouse Allergic Rhinitis Treatment
Abstract
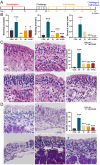
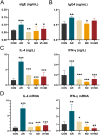
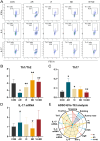
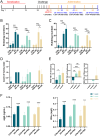
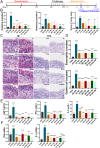
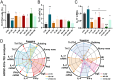
We previously found that intravenous injection of extracellular vesicles (EVs) from human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hADSC) could ameliorate allergic rhinitis (AR) in mice through immunomodulatory effects. In clinical trials, nasal delivery has been an attractive treatment for AR. We sought to determine whether there are differences in the therapeutic effects between caudal injection and their combination. We treated AR mice with ADSC-EVs via caudal vein, nasal cavity, or both. After treatment, the mice were re-sensitized and the indices of behavior, nasal mucosa morphology, and cytokine secretion of the mice under different modes of administration were calculated. The resultes show that tail vein, nasal, and combined administration could effectively relieve the inflammatory infiltration of the nasal mucosa of mice, reduce the secretion of IgE, IL-4, and other inflammatory factors, and alleviate the Th1/Th2 imbalance. Injection and nasal delivery, as well as their combination, effectively alleviated the symptoms of rhinitis in mice. Nasal administration has a better therapeutic effect when the inflammatory response is mild. It could be speculated that ADSC-EVs have excellent properties in the treatment of AR, and modes of administration can be selected for different stages of treatment in clinical therapy.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; drug administration strategy; extracellular vesicles; intranasal delivery; vein injection.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting InterestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Mardpour S, Hamidieh AA, Taleahmad S, Sharifzad F, Taghikhani A, Baharvand H. Interaction between mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles and immune cells by distinct protein content. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(6):8249–58. - PubMed
-
- Zhao R, Wang L, Wang T, Xian P, Wang H, Long Q. Inhalation of MSC-EVs is a noninvasive strategy for ameliorating acute lung injury. J Control Release. 2022;345:214–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

