Techno-economic assessment of effervescent tablet-based nanofluids
- PMID: 40179125
- PMCID: PMC11967968
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319265
Techno-economic assessment of effervescent tablet-based nanofluids
Abstract
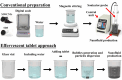
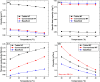
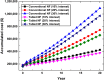
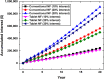
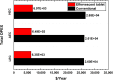
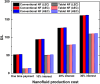
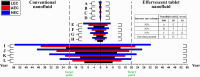
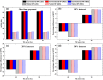
The techno-economics of producing effervescent tablet-based nanofluids in start-up industries was investigated. The thermophysical properties, equipment costs, consumables, and operational expenditures for the production methods were determined. Electrical costs for running the devices were assessed based on the lowest, average, and highest prices worldwide. Key financial metrics, including accumulated project cost, interest, annual cost, operating expenses, production cost, payback and discounted payback periods, and internal rate of return (IRR) were calculated for different interest rates and amounts of sold products. The thermal performance under laminar and turbulent flow conditions and cost effectiveness were determined. The results showed that the effervescent tablet-based nanofluid was more favourable than its conventional counterpart. This is because of the lower equipment cost for the effervescent tablet process compared to its counterpart. The interest rate showed significant influence on the annual and product costs for both types of projects. Electrical cost had a minimal impact on the previous costs for both project cases. In addition, the effervescent tablet-based project outperformed its counterpart in terms of payback period, discounted payback period, IRR, and thermal performance, making it an optimal choice for investors and decision-makers.
Copyright: © 2025 Ali et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


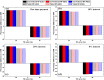
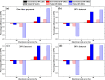
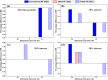
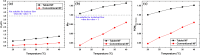

References
-
- Ali N, Teixeira JA, Addali A. Effect of water temperature, pH value, and film thickness on the wettability behaviour of copper surfaces coated with copper using EB-PVD technique. JNanoR. 2019;60:124–41. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/jnanor.60.124 - DOI
-
- Masuda H, Ebata A, Teramae K. Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles. Netsu Bussei. 1993;7(4):227–33.
-
- Choi SUS, Eastman JA. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exhibition Conference. San Francisco, CA (United States); Nov 12-17, 1995.
-
- Ali N, Teixeira J, Addali A. A review on nanofluids: Fabrication, stability, and thermophysical properties. J Nanomaterials. 2018;2018:1–33. doi: 10.1155/2018/6978130 - DOI
-
- Kalsi S, Kumar S, Kumar A, Alam T, Dobrotă D. Thermophysical properties of nanofluids and their potential applications in heat transfer enhancement: a review. Arabian J Chem. 2023;16(11):105272. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.105272 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

