NOTCH1 Mutation and Survival Analysis of Tislelizumab in Advanced or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Biomarker Analysis From the Randomized, Phase III, RATIONALE-302 Trial
- PMID: 40179324
- PMCID: PMC12118624
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO-24-01818
NOTCH1 Mutation and Survival Analysis of Tislelizumab in Advanced or Metastatic Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Biomarker Analysis From the Randomized, Phase III, RATIONALE-302 Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Although multiple agents targeting PD-1 have been approved as second-line treatment for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), only a fraction of patients derive long-term survival. Hence, reliable predictive biomarkers are urgently needed.
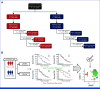
Methods: Comprehensive tumor genomic profiling and transcriptome sequencing were performed on samples from the RATIONALE-302 study. We also conducted single-cell RNA sequencing analysis on Notch1 knockdown ESCC murine models to further explore the potential molecular mechanisms underlying anti-PD-1 benefit.
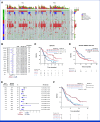
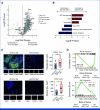
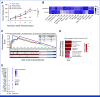
Results: We identified NOTCH1 mutation as a potential predictive biomarker for longer overall survival (OS) with tislelizumab versus chemotherapy (18.4 months v 5.3 months; hazard ratio, 0.35 [95% CI, 0.17 to 0.71]). At the transcriptional level, type I IFN (IFN-I)/toll-like receptor expression signatures were positively associated with OS benefit of tislelizumab, whereas B-cell and neutrophil signatures predicted unfavorable OS. Exploratory analyses showed that the presence of NOTCH1 mutation correlated with enrichment of IFN-I signatures and reduced infiltration of B cells and neutrophils. In murine models, comparative single-cell transcriptome analyses further revealed that Notch1 deficiency facilitated a more immunologically activated tumor microenvironment which potentiated anti-PD-1 treatment.
Conclusion: Our data provide novel insights for anti-PD-1 treatment selection using NOTCH1 mutations and may provide a rationale for combination therapy in ESCC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03430843.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
Figures

References
-
- Huang J, Xu J, Chen Y, et al. Camrelizumab versus investigator's choice of chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced or metastatic oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCORT): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:832–842. - PubMed
-
- Kato K, Cho BC, Takahashi M, et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma refractory or intolerant to previous chemotherapy (ATTRACTION-3): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:1506–1517. - PubMed
-
- Kojima T, Shah MA, Muro K, et al. Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-181 study of pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in advanced esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38:4138–4148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

