Predicting and comparing transcription start sites in single cell populations
- PMID: 40179341
- PMCID: PMC11968111
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012878
Predicting and comparing transcription start sites in single cell populations
Abstract
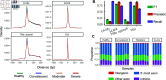
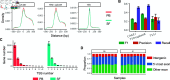
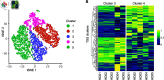
The advent of 5' single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies offers unique opportunities to identify and analyze transcription start sites (TSSs) at a single-cell resolution. These technologies have the potential to uncover the complexities of transcription initiation and alternative TSS usage across different cell types and conditions. Despite the emergence of computational methods designed to analyze 5' RNA sequencing data, current methods often lack comparative evaluations in single-cell contexts and are predominantly tailored for paired-end data, neglecting the potential of single-end data. This study introduces scTSS, a computational pipeline developed to bridge this gap by accommodating both paired-end and single-end 5' scRNA-seq data. scTSS enables joint analysis of multiple single-cell samples, starting with TSS cluster prediction and quantification, followed by differential TSS usage analysis. It employs a Binomial generalized linear mixed model to accurately and efficiently detect differential TSS usage. We demonstrate the utility of scTSS through its application in analyzing transcriptional initiation from single-cell data of two distinct diseases. The results illustrate scTSS's ability to discern alternative TSS usage between different cell types or biological conditions and to identify cell subpopulations characterized by unique TSS-level expression profiles.
Copyright: © 2025 Fu and Li. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

