Sulphostin-inspired N-phosphonopiperidones as selective covalent DPP8 and DPP9 inhibitors
- PMID: 40180908
- PMCID: PMC11968843
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-58493-z
Sulphostin-inspired N-phosphonopiperidones as selective covalent DPP8 and DPP9 inhibitors
Abstract
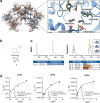
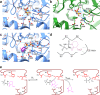
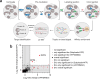
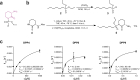
Covalent chemical probes and drugs combine unique pharmacologic properties with the availability of straightforward compound profiling technologies via chemoproteomic platforms. These advantages have fostered the development of suitable electrophilic "warheads" for systematic covalent chemical probe discovery. Despite undisputable advances in the last years, the targeted development of proteome-wide selective covalent probes remains a challenge for dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) 8 and 9 (DPP8/9), intracellular serine hydrolases of the pharmacologically relevant dipeptidyl peptidase 4 activity/structure homologues (DASH) family. Here, we show the exploration of the natural product Sulphostin, a DPP4 inhibitor, as a starting point for DPP8/9 inhibitor development. The generation of Sulphostin-inspired N-phosphonopiperidones leads to derivatives with improved DPP8/9 inhibitory potency, an enhanced proteome-wide selectivity and confirmed DPP8/9 engagement in cells, thereby representing that structural fine-tuning of the warhead's leaving group may represent a straightforward strategy for achieving target selectivity in exoproteases such as DPPs.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: A.L. is an employee of Proteros Biostructures GmbH. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang, X. & Cravatt, B. F. Chemical proteomics–guided discovery of covalent ligands for cancer proteins. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol.8, 155–175 (2024).
-
- Gehringer, M. & Laufer, S. A. Emerging and re-emerging warheads for targeted covalent inhibitors: applications in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Medicinal Chem.62, 5673–5724 (2019). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

