A randomized open label pilot study evaluating the efficacy of two dosing regimens of rifamycin SV MMX in the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
- PMID: 40181268
- PMCID: PMC11969830
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-025-03804-3
A randomized open label pilot study evaluating the efficacy of two dosing regimens of rifamycin SV MMX in the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
Abstract
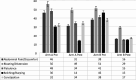
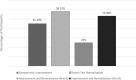
Antibiotics have demonstrated efficacy in the eradication of the underlying overgrowth bacteria and improvement of symptoms of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). The use of standard antibiotics may cause intolerable side effects such as development of multidrug-resistant enteric bacteria, Clostridioides difficile infections and dysbiosis. Nonabsorbable antibiotics have the advantage of minimized side effects. Rifaximin, an antibiotic of the ansamycin class has been shown to be effective in the treatment of SIBO. We evaluated the use of another ansamycin antibiotic, rifamycin SV MMX (AEMCOLO) in the treatment of SIBO. One difference from rifaximin is the site of delivery of AEMCOLO which appears to be the distal small intestine and colon. Hence by maintaining the microbial milieu of the proximal small intestine, the clearance of the overgrowth bacteria might be enhanced. The side effect profile of Rifamycin SV MMX has been described elsewhere in the pivotal trials; there were no safety signals noted in this study. This randomized open label pilot study evaluated the efficacy of two dosing regimens of AEMCOLO in treating SIBO. We used a simple randomization method to assign participants into study groups. The participants included 31 patients, split between two treatment arms: one receiving the medication twice daily and the other - three times daily. The outcomes were assessed based on symptom improvement and breath test normalization. The results indicated a beneficial response with both dosing regimens leading to symptom improvement and breath test normalization. Further evaluation revealed that in the three-time daily regimen, greater symptomatic improvement was observed. For clinicians treating SIBO, this study suggests that AEMCOLO is a viable treatment option. A double-blind, placebo-controlled design will probably be necessary to ascertain the true efficacy of different dosing regimens of AEMCOLO in treating SIBO.
This study was registered on ClinicialTrials.gov; clinical trial registration number: NCT04501380. Date of registration: July 28, 2020.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04501380.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by Advarra Institutional Review Board on October 2, 2019, with protocol # PRO00038302. All study subjects received and signed an informed consent form prior to participating in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Study and other materials publications: 4. We confirm that this work, including VAS questionnaires (VAS1-3) included in this protocol is original, has not been previously published elsewhere, and is not under consideration by another journal or book (print or electronic). All VAS questionnaires used in our study were developed for this study and have not been previously published elsewhere. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Pimentel M, Saad RJ, Long MD, Rao SS. ACG clinical guideline: small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Am J Gastroenterol. February 2020;115(2):165–78. 10.14309/ajg.000000000000050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

