Pan-cancer analysis identifies CLEC12A as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40181336
- PMCID: PMC11967068
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-025-03755-5
Pan-cancer analysis identifies CLEC12A as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target for lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
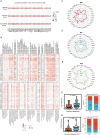
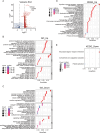
C-type lectin domain family 12 member A (CLEC12A) is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein widely expressed in innate immune cells, where it plays a crucial role in immune modulation and has been implicated in cancer progression. However, its precise function in oncogenesis and immune infiltration remains incompletely understood. To investigate this, we utilized multiple databases to assess the mRNA and protein expression levels of CLEC12A across normal tissues and a broad spectrum of cancers. We also evaluated its prognostic and diagnostic significance in pan-cancer contexts. Furthermore, the relationship between CLEC12A expression and immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoints, and immune predictors was explored. In addition, Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) and differential expression analysis were performed to examine the biological relevance of CLEC12A in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). We also leveraged various databases to predict CLEC12A's response to immunotherapy and drug sensitivity. Finally, in vitro experiments validated the functional role of CLEC12A in LUAD. Our comprehensive pan-cancer analysis revealed that CLEC12A exhibited distinct expression patterns across different cancer types, suggesting its potential as both a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker. Notably, CLEC12A expression was strongly correlated with immune cell infiltration, immune checkpoints, and immune predictors. Functional enrichment analysis highlighted that increased CLEC12A expression in LUAD was associated with a variety of immune-related biological processes and pathways. Moreover, CLEC12A showed significant predictive value for immunotherapy outcomes, and several drugs targeting CLEC12A were identified. In vitro experiments further demonstrated that CLEC12A overexpression inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells. Taken together, our findings position CLEC12A as a promising candidate for cancer detection, prognosis, and as a therapeutic target, particularly in LUAD, where it may serve as a potential target for both immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
Keywords: Biomarker; CLEC12A; Immune; LUAD; Pan-cancer; Therapy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors have read and agreed to the published the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(3):229–63. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7–34. - PubMed
-
- Li K, Zhang A, Li X, Zhang H, Zhao L. Advances in clinical immunotherapy for gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021;1876(2):188615. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

