SOX4 accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration via EZH2/NRF2 pathway in response to mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in nucleus pulposus cells
- PMID: 40181390
- PMCID: PMC11969779
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05913-1
SOX4 accelerates intervertebral disc degeneration via EZH2/NRF2 pathway in response to mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in nucleus pulposus cells
Abstract
Objective: The transcription factor SRY-related HMG-box 4 (SOX4) has been implicated in intervertebral disc diseases. This study aimed to investigate the role of SOX4 in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) and explore the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Methods: We established an IDD rat model via surgery and analyzed SOX4 expression using qRT-PCR and Western blotting. Histological evaluation, immunohistochemistry, and Safranin O staining assessed IDD progression. In vitro, an IDD cellular model was constructed using IL-1β-stimulated nucleus pulposus (NP) cells. SOX4 knockdown and overexpression experiments in NP cells examined SOX4 effects on ECM degradation, NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis, and mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The involvement of the EZH2/NRF2 pathway in SOX4-mediated NLRP3 activation was also examined.
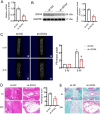
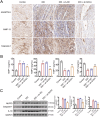
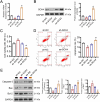
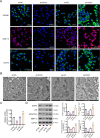
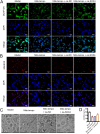
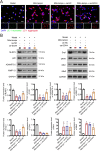
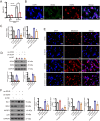
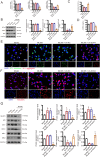
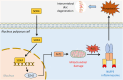
Results: SOX4 expression was significantly increased in IDD rats and promoted IDD progression. Knockdown of SOX4 inhibited ECM degradation and NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in NP cells. In vitro experiments showed that SOX4 promoted ECM degradation by upregulating MMPs and ADAMTS-5 expression, and suppressed collagen II and aggrecan synthesis. SOX4 knockdown inhibited NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis, while overexpression accelerated it in NP cells. Additionally, SOX4 was found to exacerbate mitochondrial ROS-dependent NLRP3 inflammasome activation in NP cells. Further investigation revealed that SOX4 enhanced NLRP3 inflammasome activation by upregulating EZH2 expression and modulating the EZH2/NRF2 pathway, with EZH2 inhibition attenuating SOX4-induced NLRP3 activation.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that SOX4 accelerates IDD progression by promoting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via modulating the EZH2/NRF2 pathway, leading to NP cell pyroptosis and ECM degradation. Targeting SOX4 may represent a potential therapeutic strategy for treating IDD.
Keywords: EZH2/NRF2 pathway; Extracellular matrix degradation; Intervertebral disc degeneration; NLRP3 inflammasome activation; Pyroptosis; SRY-related HMG-box 4.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Yangzhou University (No. 202306014). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EZH2-H3K27me3-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing of DKK1 Induces Nucleus Pulposus Cell Pyroptosis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Activating NLRP3 and NAIP/NLRC4.Inflammation. 2025 Apr;48(2):902-918. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02096-1. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39052181
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting the IRF2/POSTN/Notch1 axis in nucleus pulposus cells for intervertebral disc degeneration.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Jan 22;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03335-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 39844302 Free PMC article.
-
Maltol ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway and regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Feb;31(1):369-384. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01098-5. Epub 2022 Nov 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36401729 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Pyroptosis in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration and Its Therapeutic Implications.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 2;12(12):1804. doi: 10.3390/biom12121804. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic mechanisms of icariin in intervertebral disc degeneration: A critical narrative review.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 May 15;42:102047. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102047. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40486496 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptotic Pathway in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: From Molecular Pathways to Clinical Interventions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;15(12):1510. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15121510. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40564831 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

